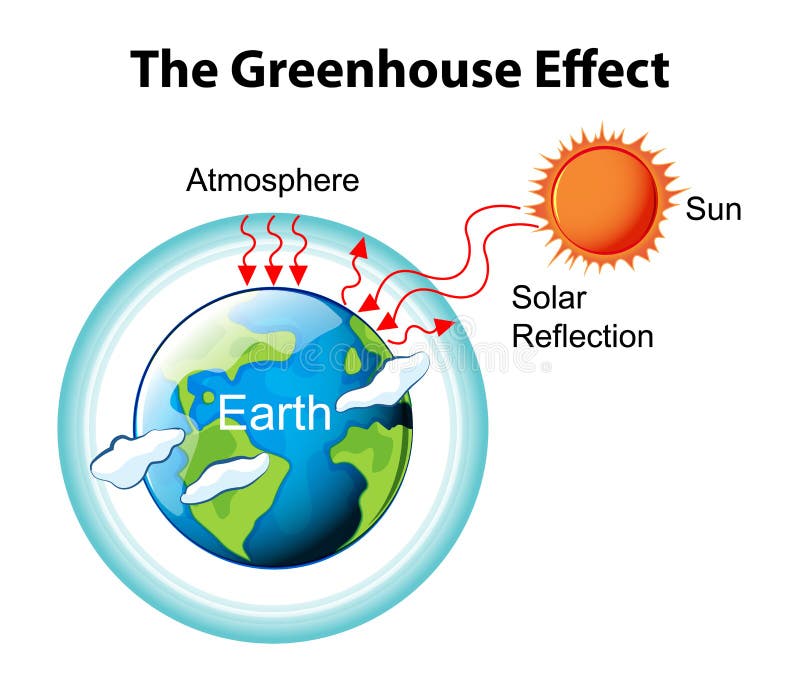
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – depends on the amount of greenhouse gases
c News
Greenhouse effect diagram greenhouse gases
Greenhouse effect diagram greenhouse gases-The diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphereFigure 71 Rise in the concentrations of greenhouse gases since the 18th century As we will see in section 73, simple theory shows that a rise in greenhouse gases should result in surface warming;




Greenhouse Effect Vector Diagram Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
The enhanced greenhouse effect What has scientists concerned now is that over the past 250 years, humans have been artificially raising the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere at an everincreasing rate, mostly by burning fossil fuels, but also from cutting down carbonabsorbing forestsChange the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes Then compare to the effect of glass panes Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?How do greenhouse gases affect the climate?
Learners need to be aware that the Greenhouse Effect is a beneficial, natural process and that without it the Earth would be too cold to sustain life Now introduce the idea of global warming Have all the remaining students put on "Greenhouse Gases" name tags and have them join the other "Gases" in the middle of the roomThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight Unlike those more abundant gases though, greenhouse gases are not transparent to heat (longwave infrared radiation) The sunwarmed surface of Earth radiates heat day and night
The greenhouse effect on other planets Because the greenhouse effect is a natural process, it affects other bodies in the solar system, too And, in some cases, that provides a warning about howThe natural greenhouse effect The effect of increased greenhouse gas concentrations The greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into space Besides CO 2 there are other greenhouse gases These include water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone These include water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Without any greenhouse gases, Earth would be an icy wasteland




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician JosephT he greenhouse effect is the name applied to the process which causes the surface of the Earth to be warmer than it would have been in the absence of an atmosphere (Unfortunately, the name, greenhouse effect is a misnomer more on that later) Global warming is the name given to an expected increase in the magnitude of the greenhouseGreenhouse gas Water vapor and clouds cause most of the Earth's natural greenhouse effect and account for about 90% of the total heatretaining capacity of the atmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, trapping the heat in our atmosphere instead of letting it escape to space



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 149 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around the world, greenhouse gases become globally mixed, which means the concentration of a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide is roughly the same no matterThe natural atmosphere is composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 09% argon, and only about 01% natural greenhouse gases Although a small amount, these greenhouse gases make a big difference they are the gases that allow the greenhouse effect to exist by trapping in some heat that would otherwise escape to spaceGreenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth This process maintains the Earth's temperature at around 33 degrees Celsius warmer than it would otherwise be, allowing life on Earth to exist Enhanced greenhouse effect




Greenhouse Effect Vector Diagram Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
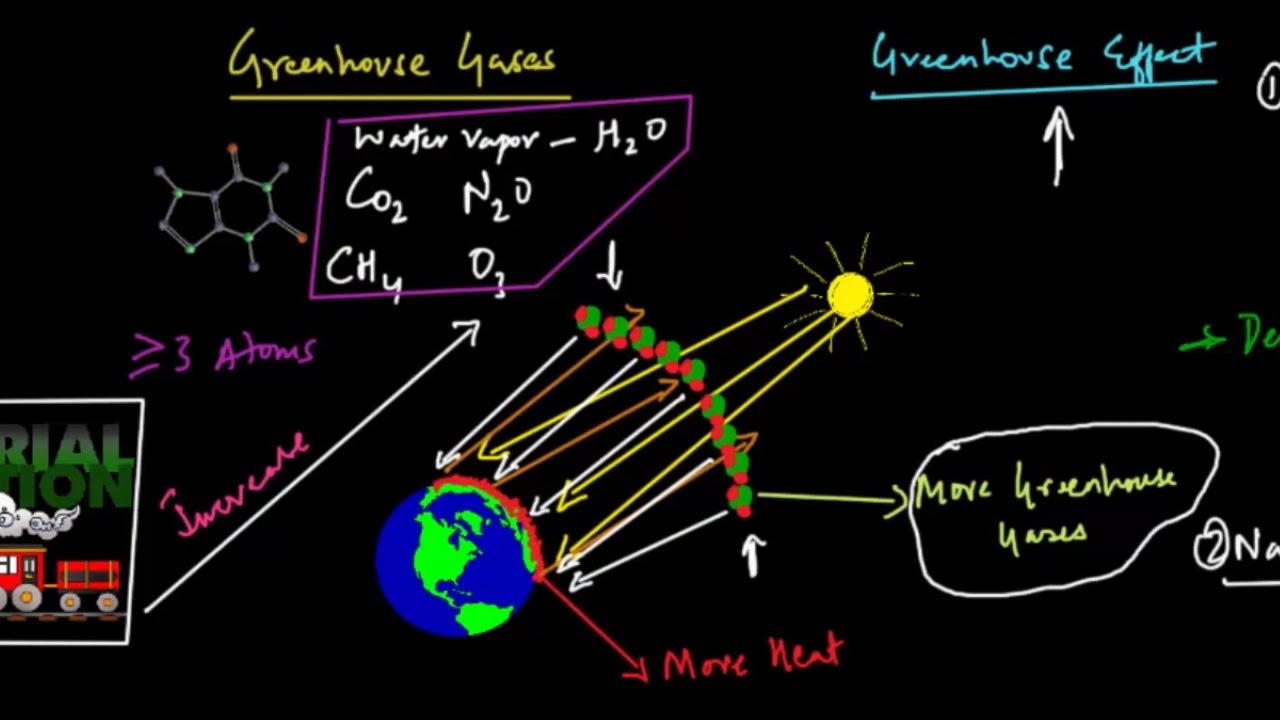



Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube
When we add extra greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, though, we increase the atmosphere's heattrapping capacity Less heat escapes to space, more returns to Earth, and the planet warms There's really no scientific doubt about this process, which is known as the greenhouse effect What scientists don't know is exactly how strong the Although greenhouse gases make up only about 1 percent of the Earth's atmosphere, they regulate our climate by trapping heat and holding it in a kind of warmair blanket that surrounds the planetThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist
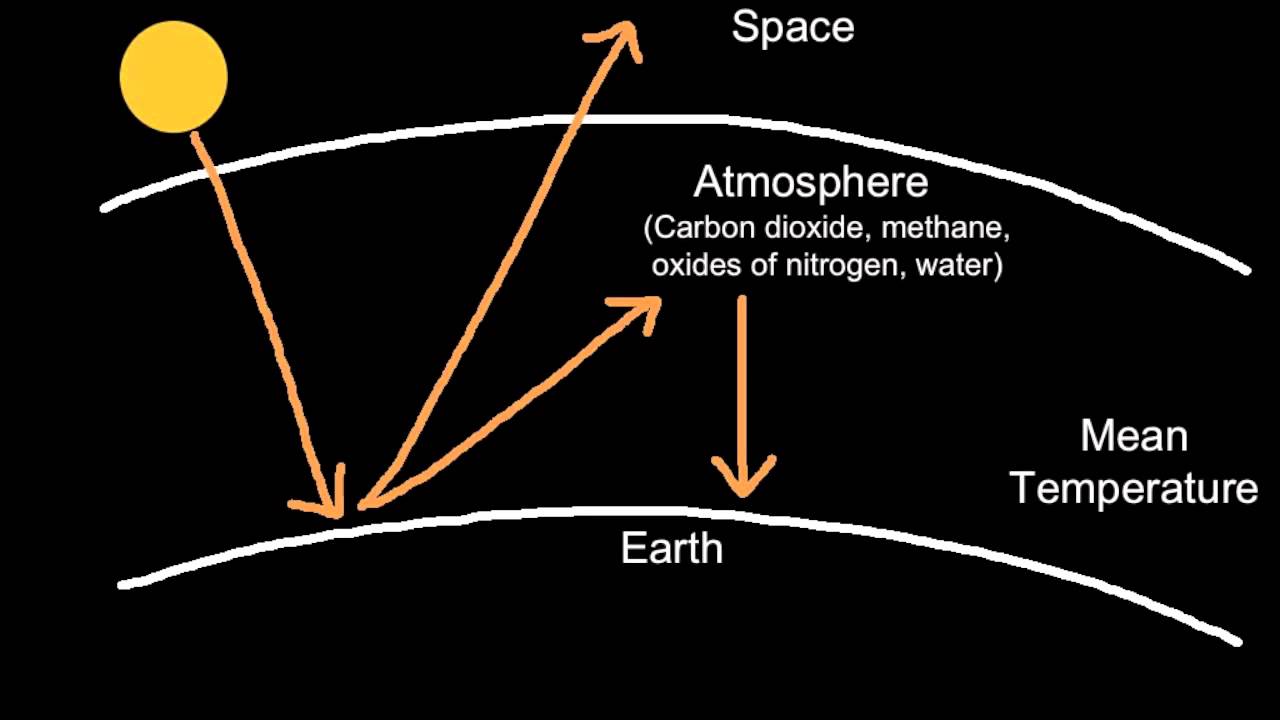



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
Important Greenhouse Gases (concentrations in parts per million volume) water vapor 0140,000 carbon dioxide 370 methane 17 nitrous oxide 03 ozone 001 chlorofluorocarbons ~ A greenhouse gas is defined as a gas that absorbs significantly the radiation emitted by the Earth and its atmosphere (Infrared, IR, or longwave radiation)Simple diagram of greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases are gases in an atmosphere that absorb and emit radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The main greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneIn our solar system, the atmospheres ofThe greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F) The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would be




Agriculture And Climate Change Nrcs South Dakota




What Is Greenhouse Effect Labeled Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng
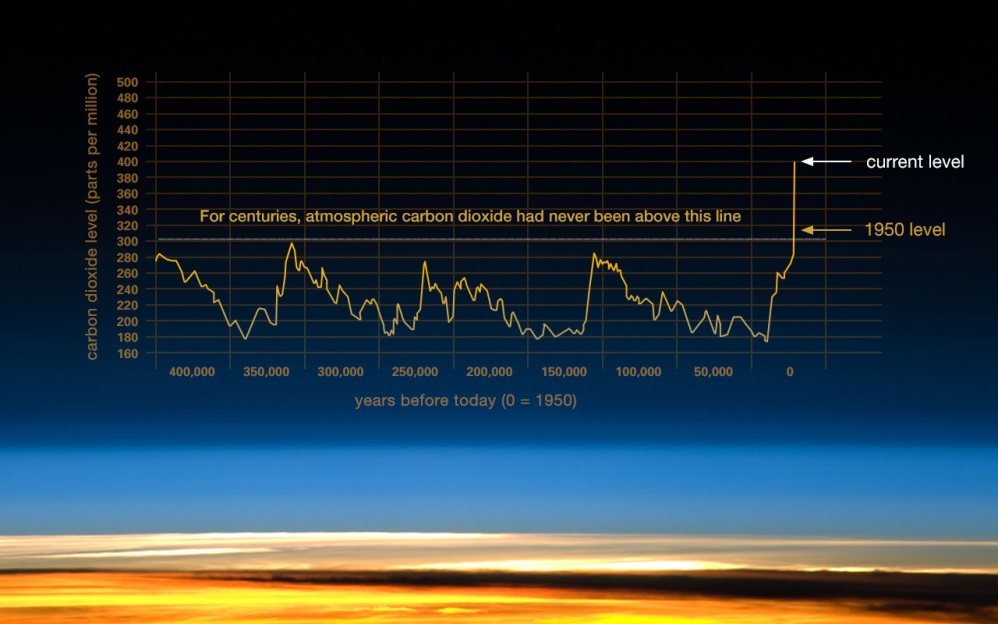
Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does not Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth's atmosphereAccording to National geographic " Atmospheric levels of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide are now higher than at any time in the last 800,000 years"
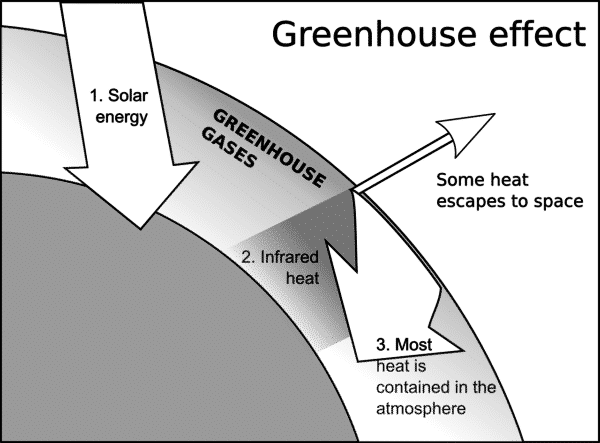



What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub



c News
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over timeTo the right is a diagram (also from NOAA, ESRL, the same source as the table above) which illustrates the greenhouse effect Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (round about the late 1700's), the concentration of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere has rocketed by an estimate of 30%, most significantly carbon dioxide The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally,




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



Causes And Greenhouse Effect
This greenhouse effect, which is probably better described as warming produced by heattrapping gases, is incredibly powerful — it returns more energy to the surface than we absorb from the Sun, and its strength is closely tied to the global carbon cycle, andThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect worksThe greenhouse effect Another group of greenhouse gases includes the chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) CFCs have been responsible for depleting the ozone layer as they attack and destroy ozone molecules
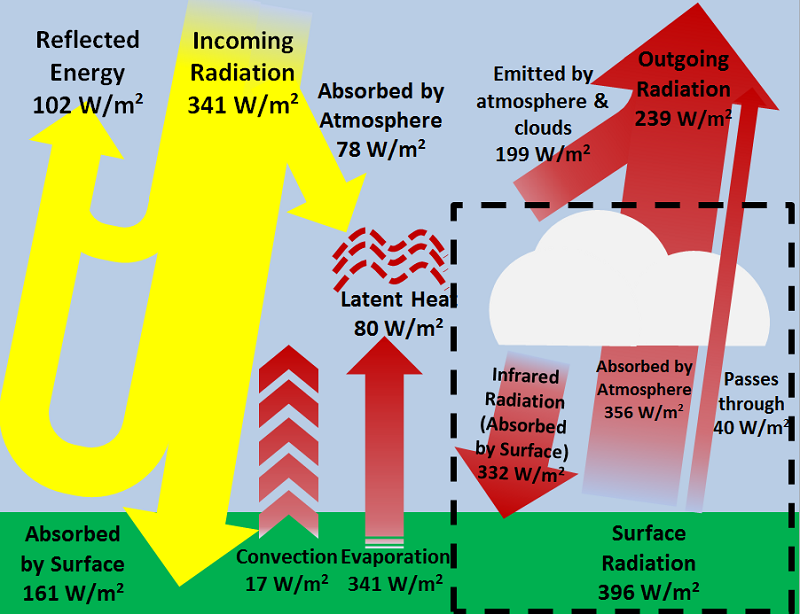



The Greenhouse Effect And Earth S Energy Budget Energy Education




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3) Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface wouldThe greenhouse effect is a natural process responsible for keeping the earth at the temperature needed to sustain life Acting just like the glass walls of a greenhouse, gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap the sun's heat in the atmosphere and prevent itThe greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is reradiated in all directions Since part of this reradiation is back towards the surface and the lower atmosphere, it results in an elevation of the average surface temperature above what it would be in




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change
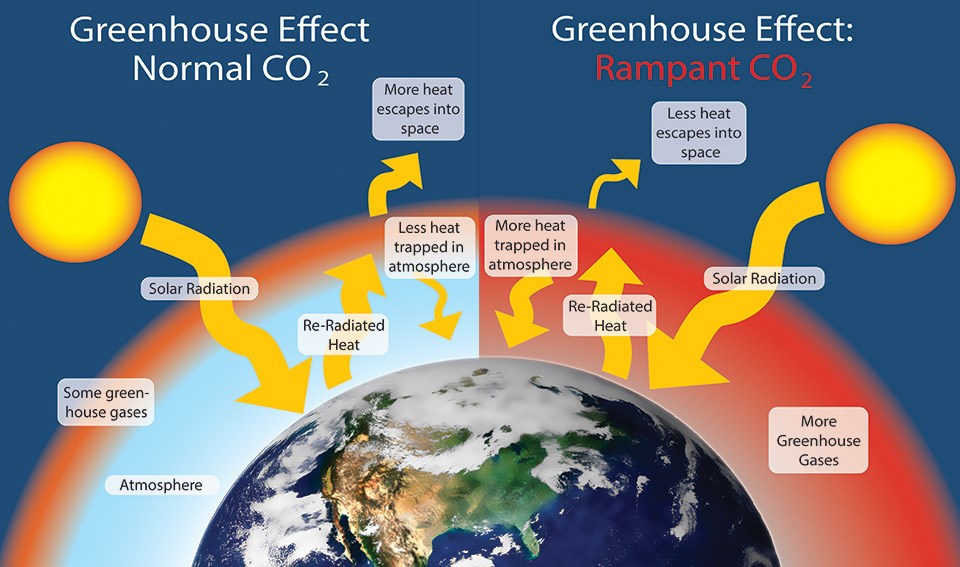



What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service
The uncertainty lies in the magnitude of the response It is well established that the global mean surface temperature of the Earth has increased over the past century by about 06 K Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect En la gráfica se comparan los cambios en la temperatura de la superficie global (línea roja) y la energía del Sol que recibe la Tierra (línea amarilla) en vatios (unidades de energía) por metro cuadrado desde 10That approach in effect makes carbon dioxide, CO 2, the prevailing "currency" of greenhouse gases and global warming Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC)
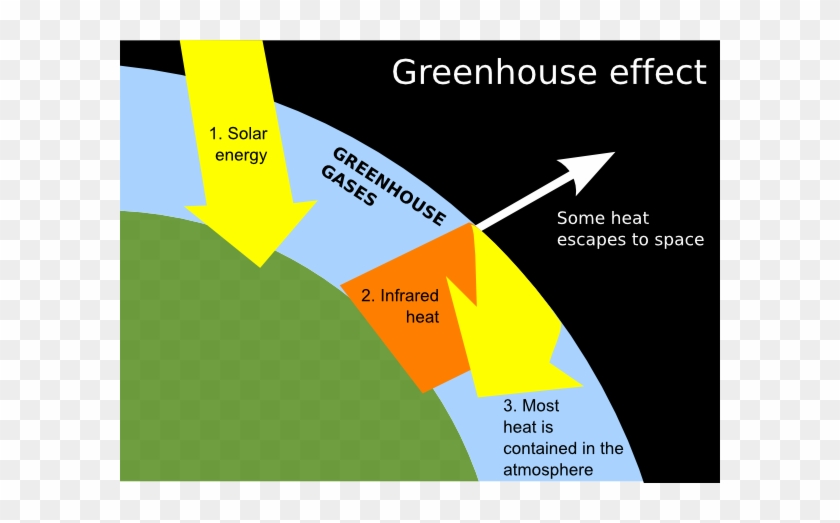



Greenhouse Clip Art At Clker Greenhouse Effect Labelled Diagram Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download
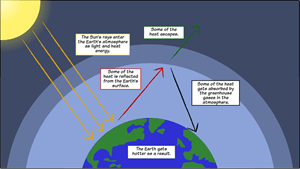



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gases Some major greenhouse gases that cause the greenhouse effect They include Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Methane (CH4) Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Ozone (O3) Water vapor (H2O) CFCs; The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some of




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education




The Greenhouse Effect Explained
Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation , etc The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount of these gases The main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor (which all occur naturally), and fluorinated gases Tyndall soon established that carbon dioxide and water vapour were among the gases that absorbed heat, and also that they radiated heat, the physical basis of the greenhouse effect In making these discoveries, Tyndall set the foundation for our modern understanding of the greenhouse effect, climate change, meteorology, and weather



How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effectIn terms of the net increase in the greenhouse effect due to humanproduced greenhouse gases, CO 2 is responsible for the lion's share CO 2 from fossil fuel burning alone is more than half the net force If you add CO 2 from fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and other minor sources, this comes to a little more than threefourths of the net Greenhouse effect is nothing but the process by which radiation from the planet's atmosphere warms up its surface to a temperature above the atmospheric level The thermal radiation from earth's surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directions




The Greenhouse Effect World101



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram
The greenhouse effect keeps the temperatures on our planet mild and suitable for living things Greenhouse gases (GHG) include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases These molecules in our atmosphere are called greenhouse gasesExplore the atmosphere during the ice age and today What happens when you add clouds?Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




What Is The Greenhouse Effect And Why It S Currently Bad For Us



1




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 149 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences



Greenhouse Gases




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



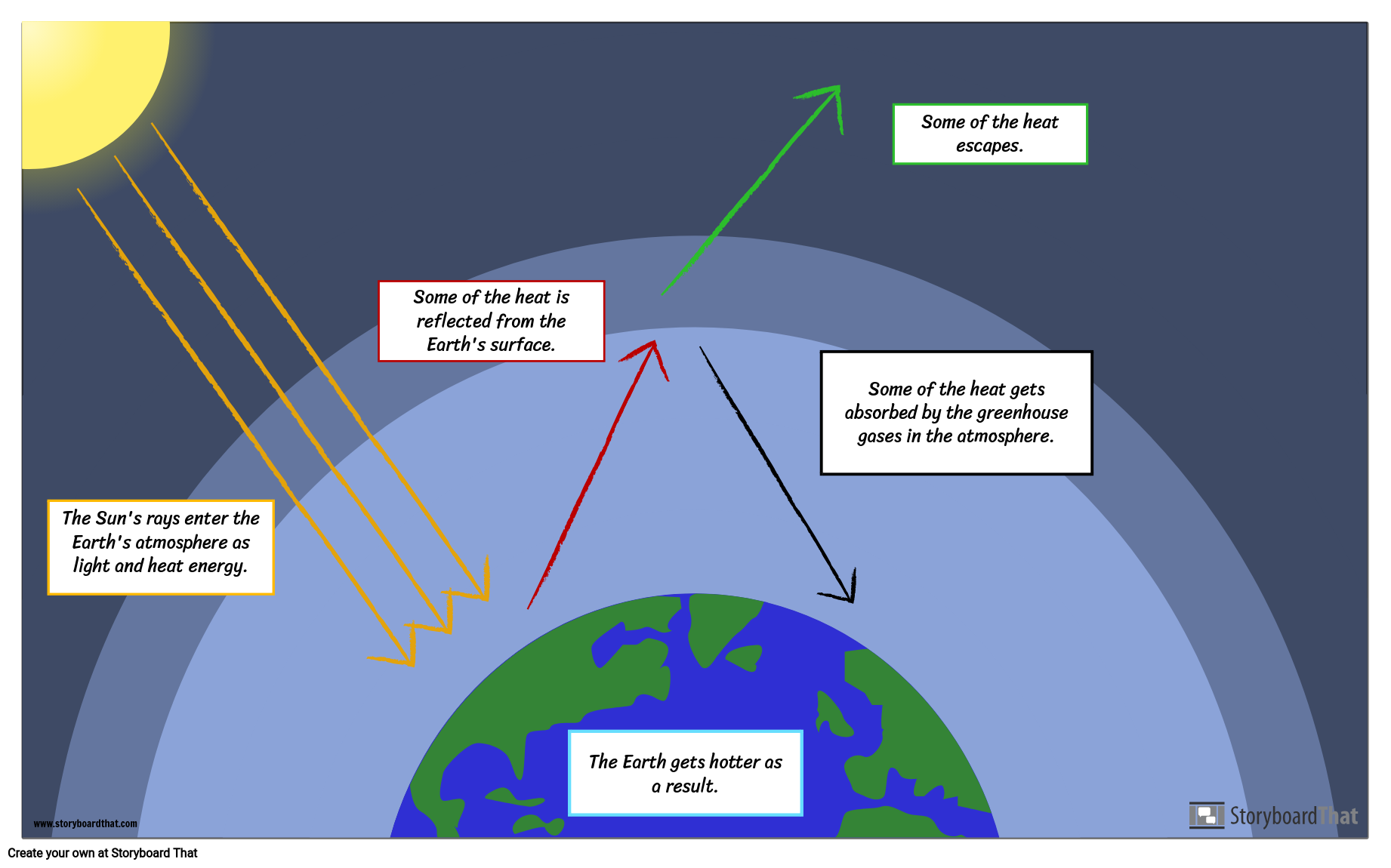
How The Greenhouse Effect Works The Diagrams Of Two Chegg Com




The Greenhouse Effect
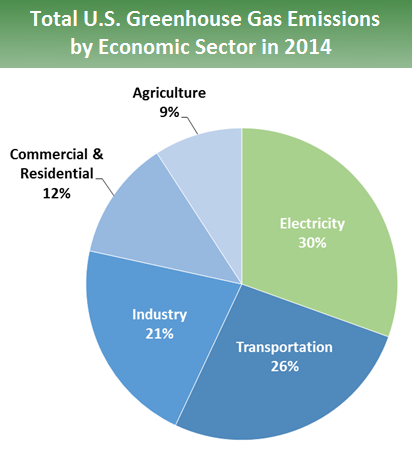



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
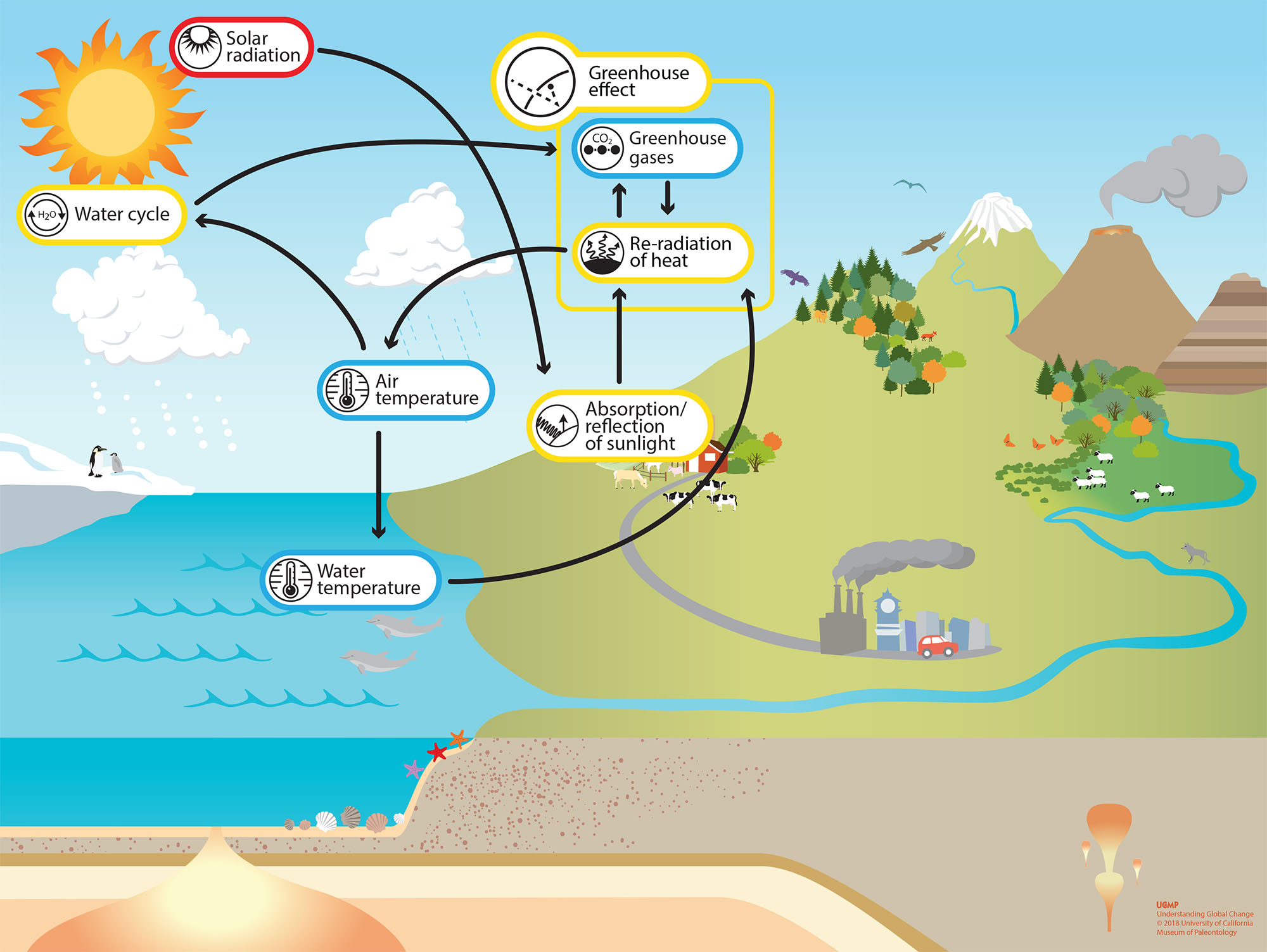



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




Greenhouse Effect Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download



1




File Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Wikimedia Commons




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated



Chart Eu And Us Slash Greenhouse Gas Emissions Statista




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



Http Www Manhassetschools Org Cms Lib8 Ny Centricity Domain 709 Greenhouse student Pdf




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
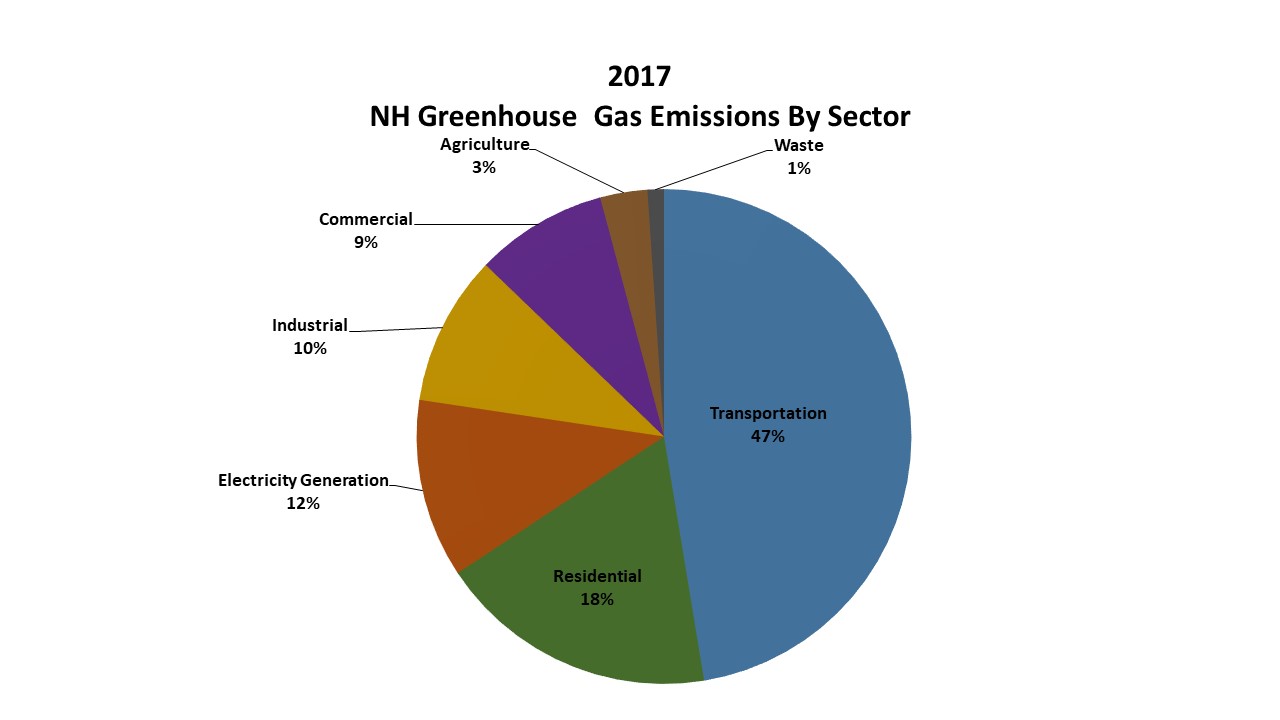



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Nh Department Of Environmental Services
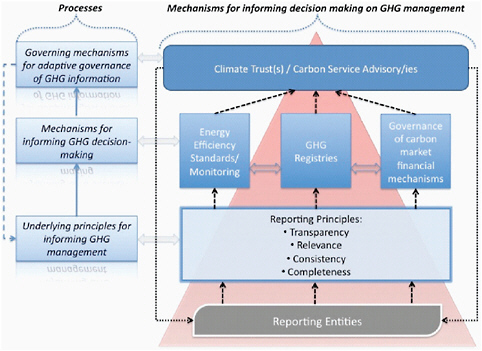



6 Informing Greenhouse Gas Management Informing An Effective Response To Climate Change The National Academies Press
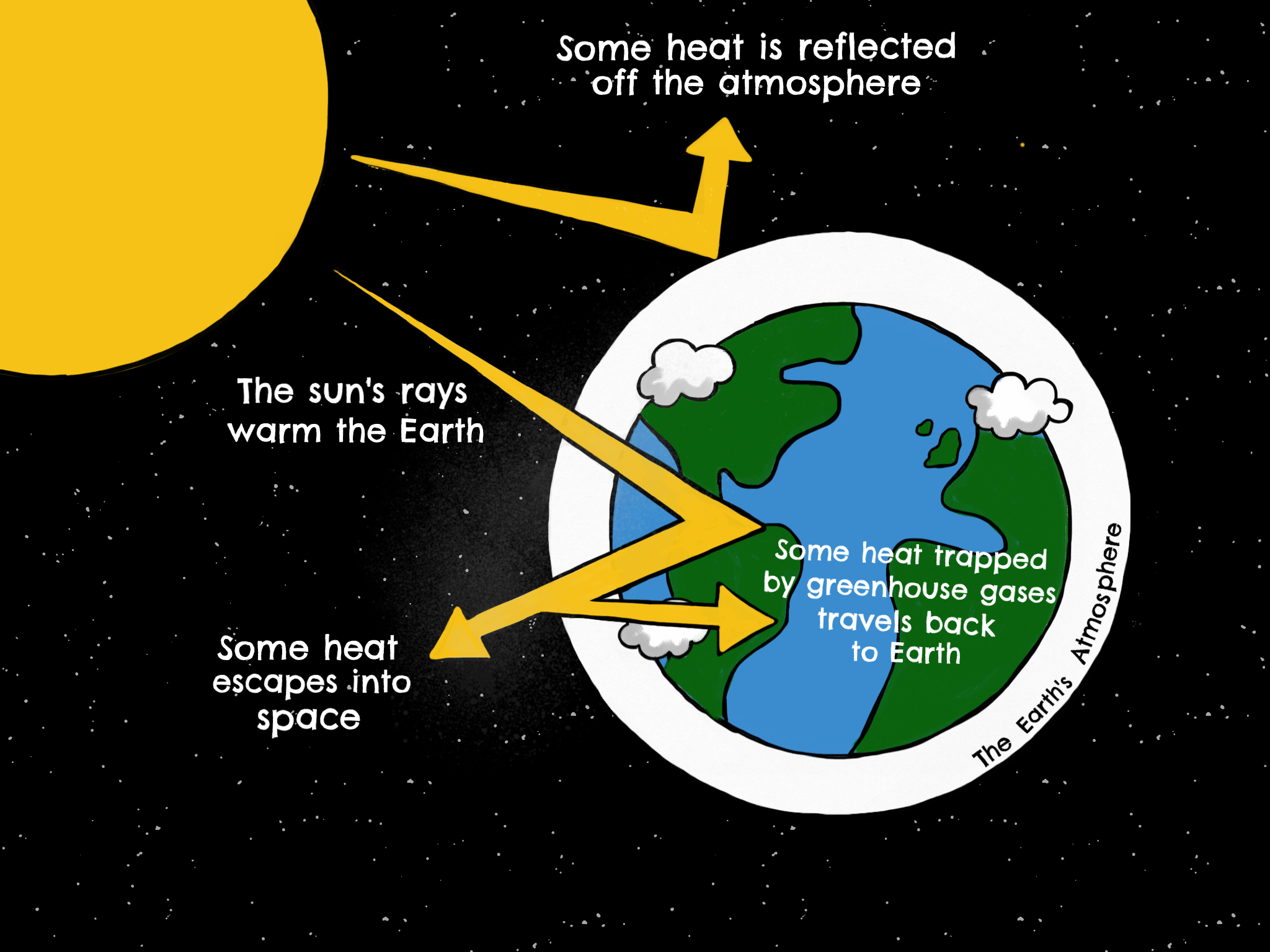



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help



3




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/assets/4250823/ecofys-world-ghg-emissions-flowchart.png)



Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Vox




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Climate Change Basics Ag Matters




Understanding The Greenhouse Effect Sciencemusicvideos



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
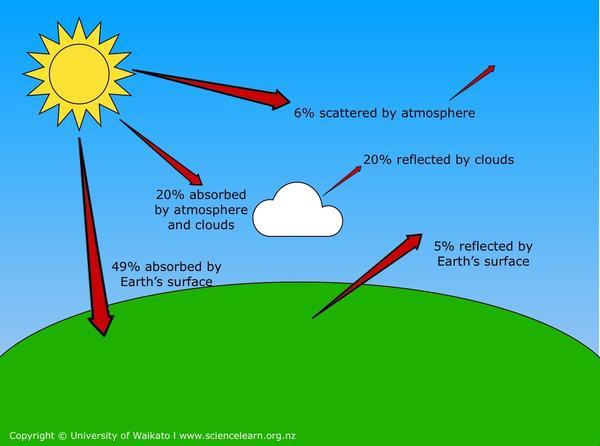



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub



3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network
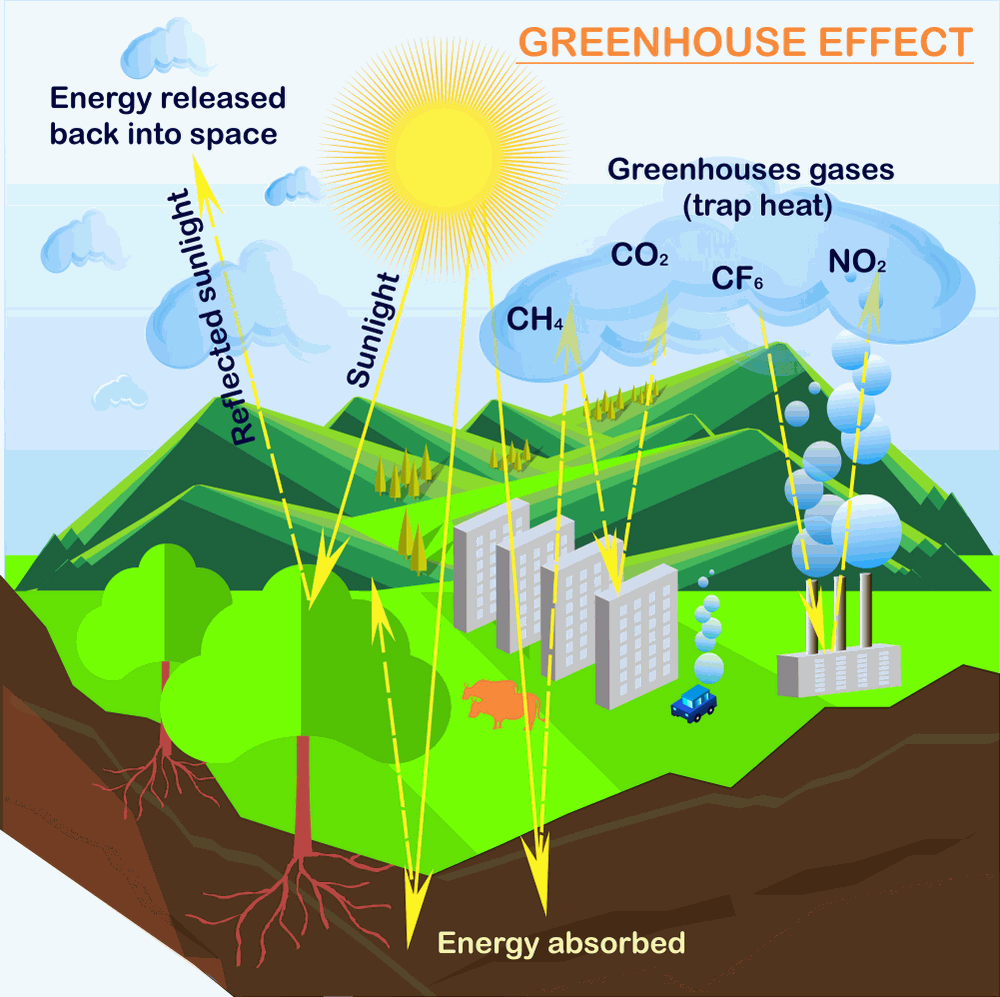



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering



What Are Greenhouse Gases Environnet
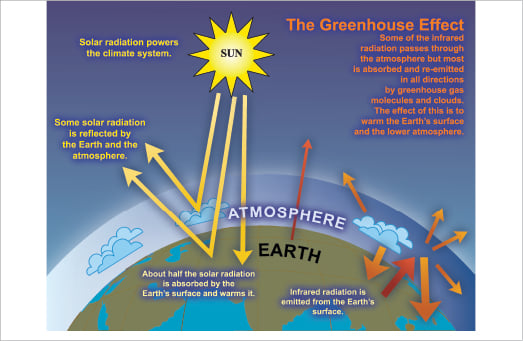



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science
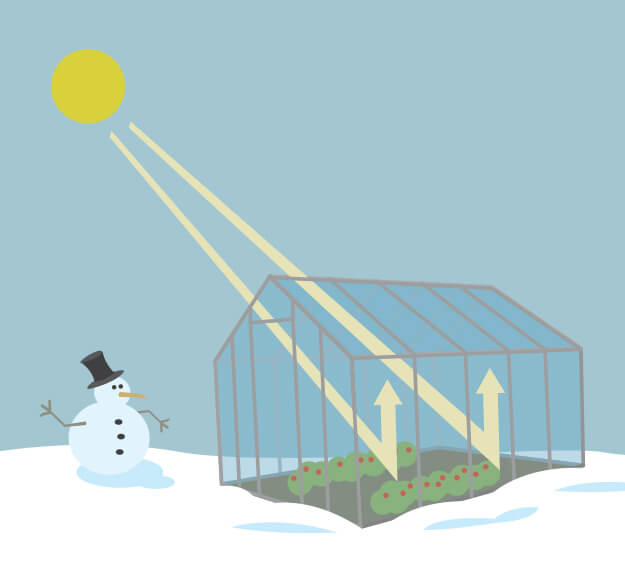




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




12 160 Greenhouse Effect Stock Photos And Images 123rf
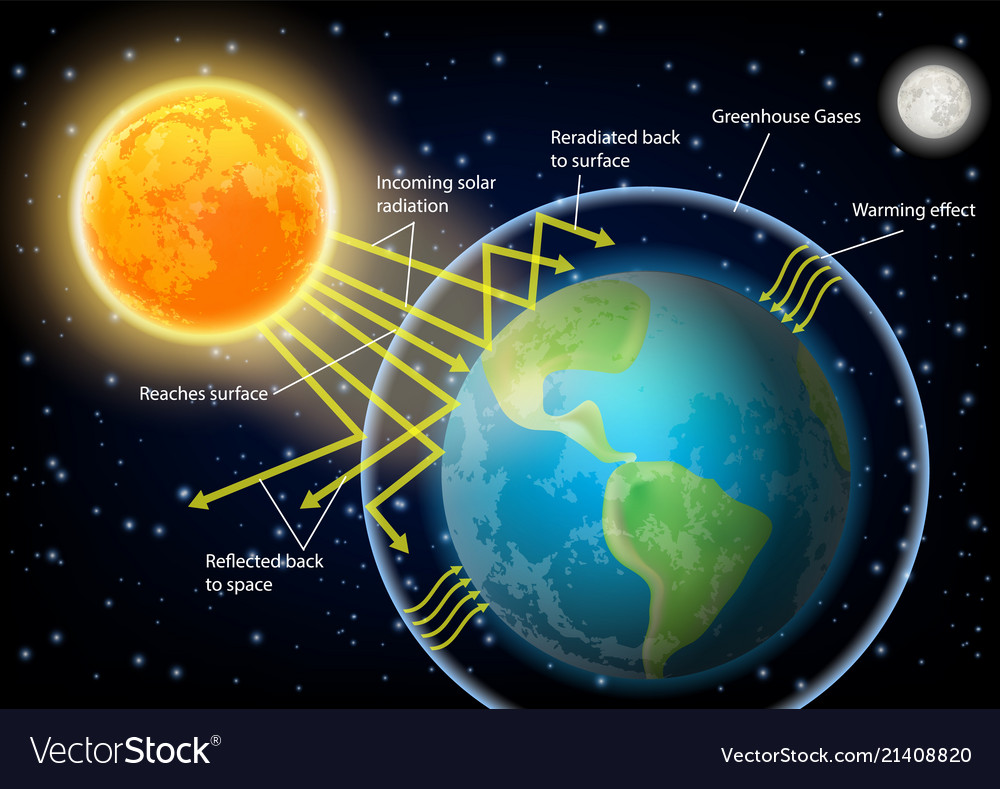



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/assets/4250823/ecofys-world-ghg-emissions-flowchart.png)



Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Vox
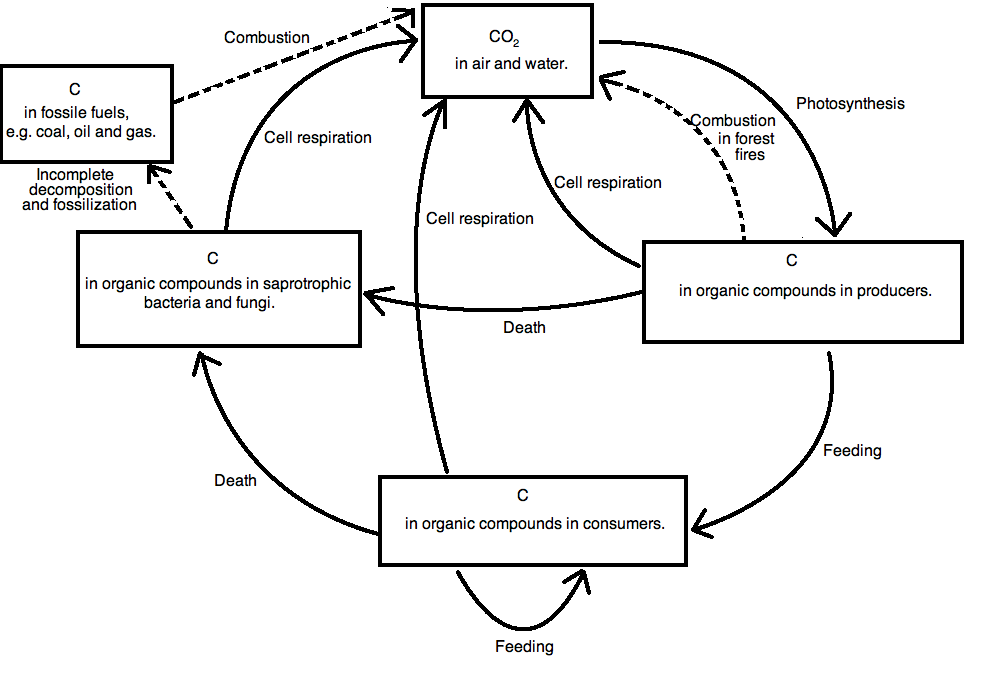



Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect




The Diagram Below Shows A Model Of The Greenhouse Effect Which Would Happen More If There Were No Brainly Com




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram
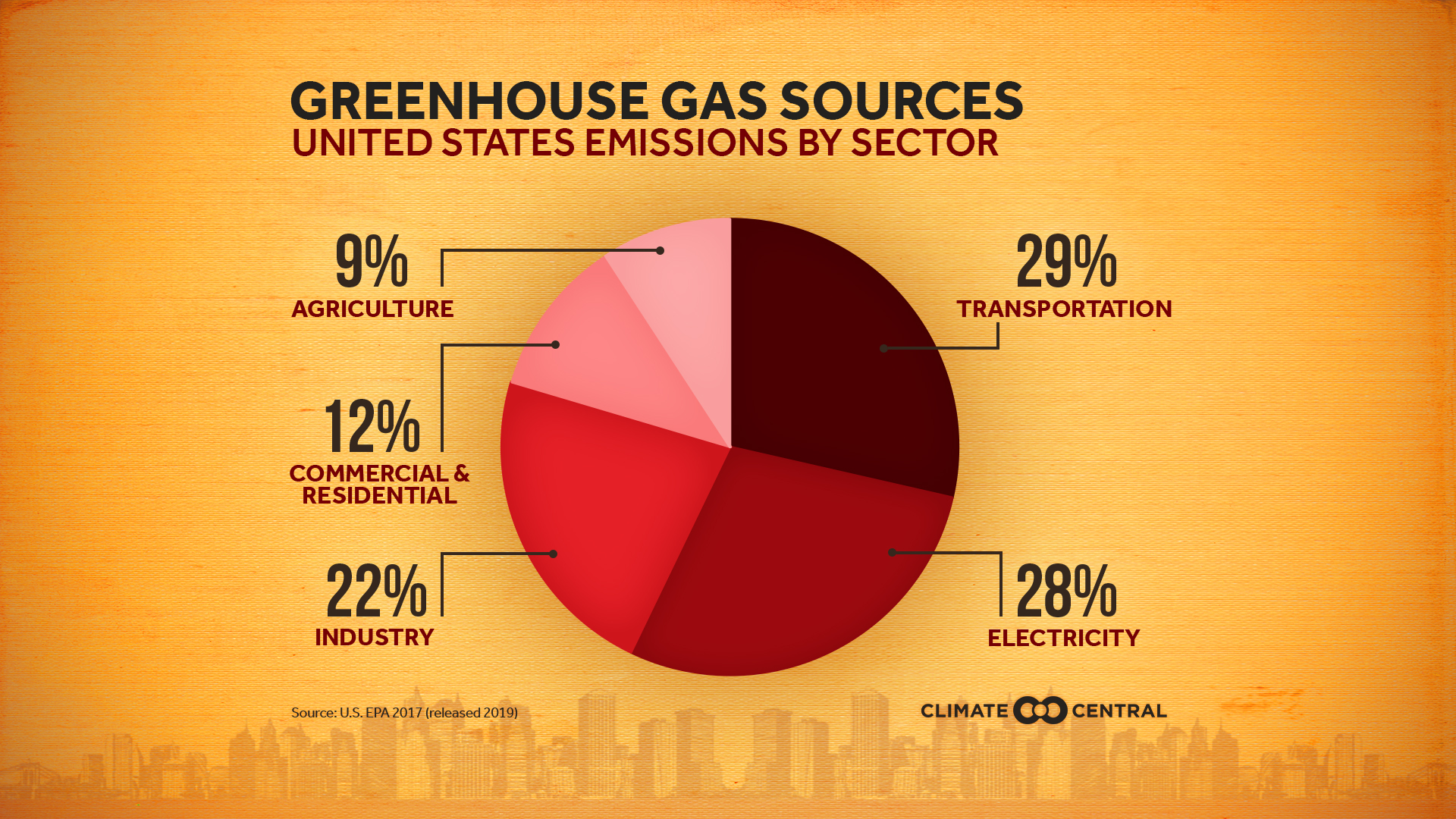



Emissions Sources Climate Central




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect World101




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
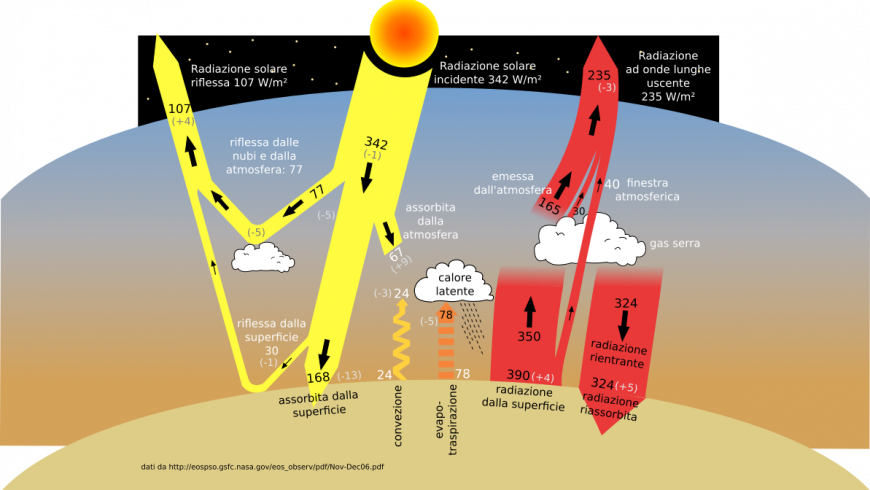



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa



The Following Diagram Shows How Greenhouse Gases Trap Energy From The Sun Ielts Training Tips Ielts Training Ernakulam Kerala India



Effects Greenhouse Effect




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿