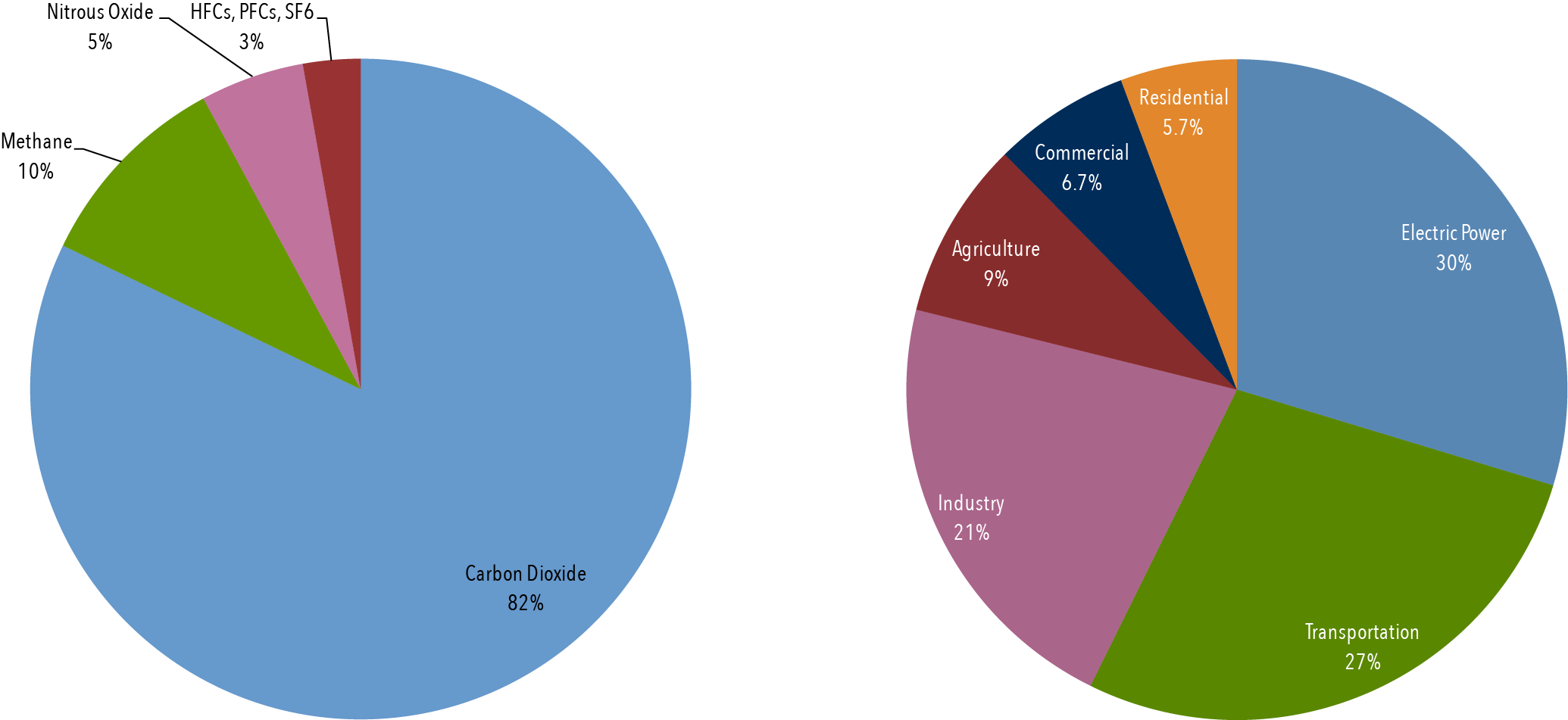
Noun phenomenon where gases allow sunlight to enter Earth's atmosphere but make it difficult for heat to escape greenhouse gas Noun gas in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and ozone, that absorbs solar heat reflected by the surface of the Earth, warming the atmosphereIndustry (21% of 10 global greenhouse gas emissions) Greenhouse gas emissions from industry primarily involve fossil fuels burned on site at facilities Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere related to human activities Its concentration reached new highs in 18 of 4078 ppm, or 147 percent of pre

Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere graph
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere graph- The graphs show monthly mean carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii The carbon dioxide data on Mauna Loa constitute the longest record of direct measurements of CO 2 in the atmosphere They were started by C David Keeling of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in March of 1958 at a facility of the National Oceanic andLargely caused by the humaninduced increase of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere The data in this graph show that temperatures have risen and fallen with CO2 concentrations over the last 400,000 years More recent data have shown the same relationship extends 650, 000 years or more Gas
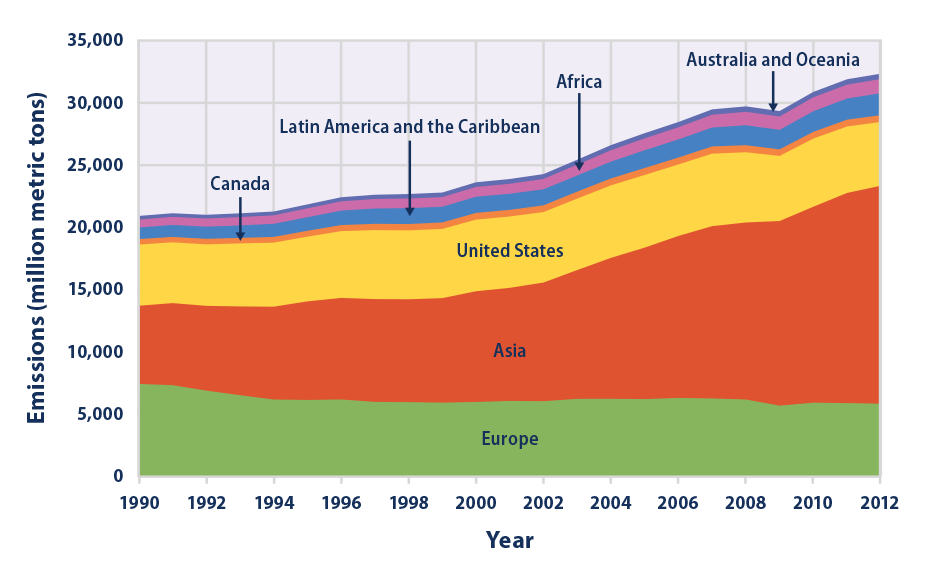



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
Cattle are the No 1 agricultural source of greenhouse gases worldwide Each year, a single cow will belch about 2 pounds of methane Methane from cattle is shorter lived than carbon dioxide but 28 times more potent in warming the atmosphere, said Mitloehner, a professor and air quality specialist in the Department of Animal Science Methane, a powerful greenhouse gas which remains in the atmosphere for less than a decade, was 260% of preindustrial levels in 19 at 1 877 parts per billion The increase from 18 to 19 was Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an important heattrapping (greenhouse) gas, which is released through human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels, as well as natural processes such as respiration and volcanic eruptions The first graph shows atmospheric CO 2 levels measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, in recent years, with average seasonal cycle
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the makeup of our atmosphere Earth is sometimes called the "Goldilocks" planet – it's not too hot, not too cold, and the conditions are just right to allow life, including us, to flourish (Graph ESRL NOAA) This curve is often used to show the direct link between rising atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations and rising temperatures across the globe A similar dataset – though not as long as the Mauna Loa dataset – is provided by measurements carried out at Jungfraujoch here in Switzerland (see next figure) Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities In 14, CO 2 accounted for about 809% of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and
Electricity and Heat Production (25% of 10 global greenhouse gas emissions) The burning of coal, natural gas, and oil for electricity and heat is the largest single source of global greenhouse gas emissions;The following list shows the greenhouse gasses and the source of emission Carbon dioxide (CO2) Energy related CO2 % and Other CO2 2% Produced by combustion of solid waste, fossil fuels, and wood and wood products Methane (CH4) 9% Source is the production and transport of coal, natural gas, and oil Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and certain synthetic chemicals, trap some of the Earth's outgoing energy, thus retaining heat in the atmosphere This heat trapping causes changes in the radiative balance of the Earth—the balance between energy received from the sun and emitted from Earth—that alter climate




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov
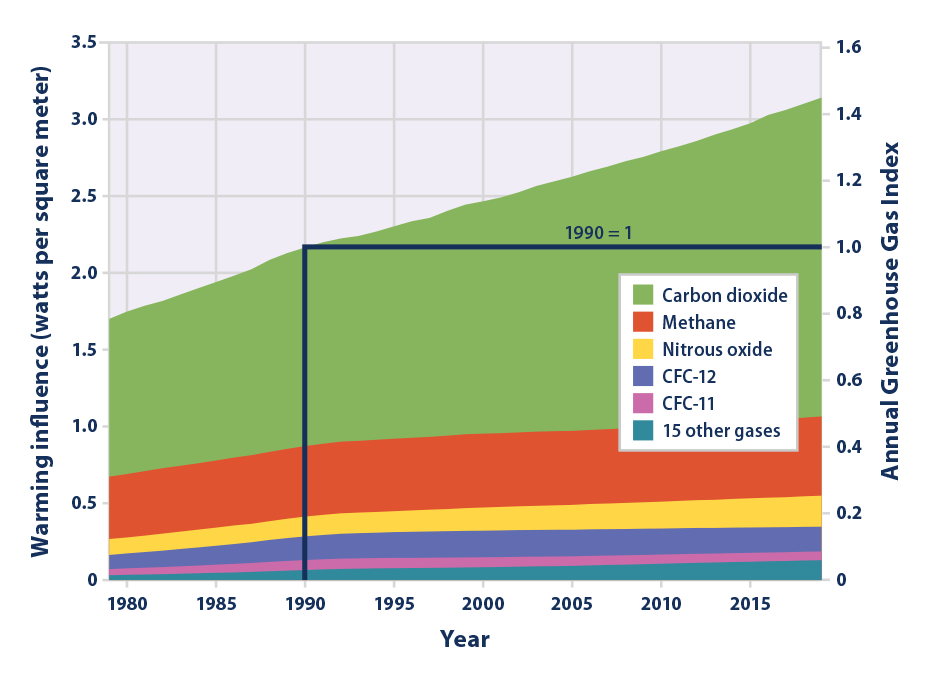
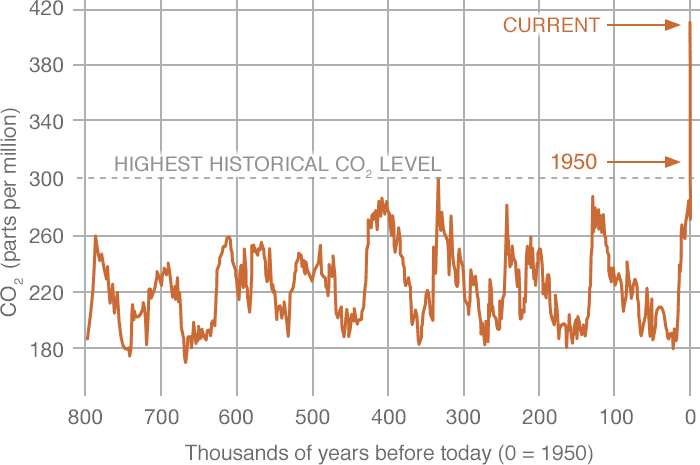
Data for the past 00 years show that the atmospheric concentrations of CO 2, CH 4, and N 2 O – three important longlived greenhouse gases – have increased substantially since about 1750 Rates of increase in levels of these gases are dramatic CO 2, for instance, never increased more than 30 ppm during any previous 1,000year period in this record but has already risen by 30 Earth's lower atmosphere (the troposphere) is comprised of greenhouse gases and nongreenhouse gases in different concentrations As you can see in the pie graph pictured on the right, the lower atmosphere is made mostly of nitrogen(N 2) and oxygen(O 2) gas moleculesWhile both nitrogen and oxygen are important in supporting life on Earth, they are not greenhouse gasesThis graph shows the heating imbalance in watts per square meter relative to the year 1750 caused by all major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12, and a group of 15 other minor contributors




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




Global Warming
1 Carefully study the data given in the above table to realize the increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere since they are not a dununy data set, they are real data 2 Plot the data on graph paper, time on the horizontal axis and gas concentration on the vertical axis 3Greenhouse gases trap heat and make the planet warmer CO2 is a greenhouse gas but there are many other, and stronger greenhouse gases than CO2 The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere include Water vapor The main greenhouse gas, contributing 3672 % of the greenhouse effect This graph depicts the upward trajectory of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere as measured at the Mauna Loa Atmospheric Baseline Observatory by NOAA and the Scripps Institution of Oceanography The annual fluctuation is known as the Keeling Curve noted that CO 2 is by far the most abundant humancaused greenhouse gas,



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
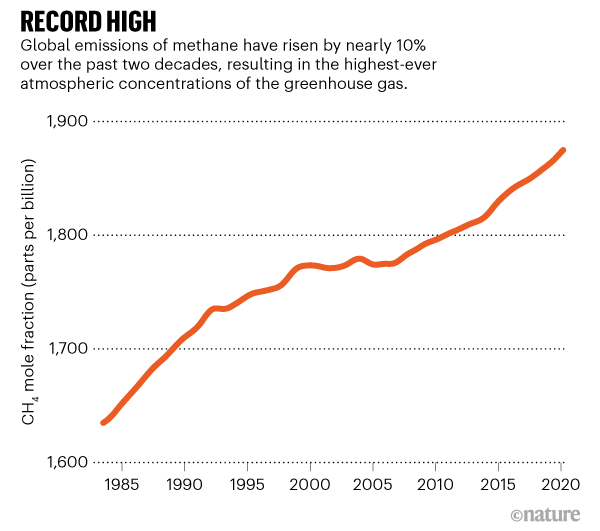



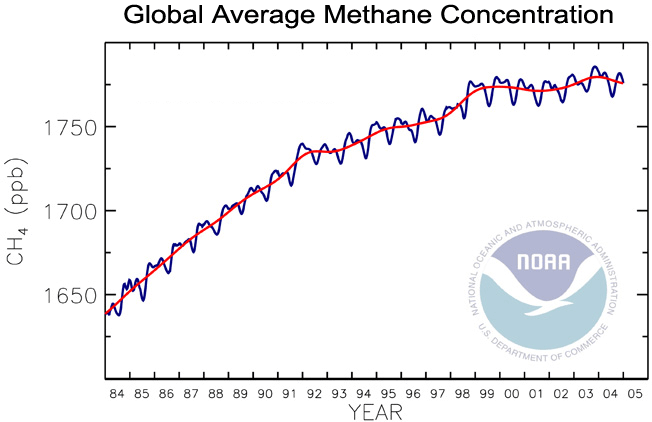
Global Methane Levels Soar To Record High
You can view graphs showing how the amount of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and various chlorofluorocarbons have changed over time at any NOAA sampling site Additional data such as isotopic ratios of carbon and oxygen species and solar radiation areThe majority of the Earth's atmosphere is composed of a mixture of only a few gasesnitrogen, oxygen, and argon;"Dumping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere makes the atmosphere more humid And since water vapor is itself a greenhouse gas, the increase in humidity amplifies the warming from carbon dioxide" Specifically, the team found that if Earth warms 18 degrees Fahrenheit, the associated increase in water vapor will trap an extra 2 Watts of




The Science Of Carbon Dioxide And Climate




Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnes This indicator describes how the levels of major greenhouse gases in the atmosphere have changed over time Figure 1 Global Atmospheric Concentrations of Carbon Dioxide Over Time This figure shows concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere from hundreds of thousands of years ago through 19, measured in parts per million (ppm)Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities In 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
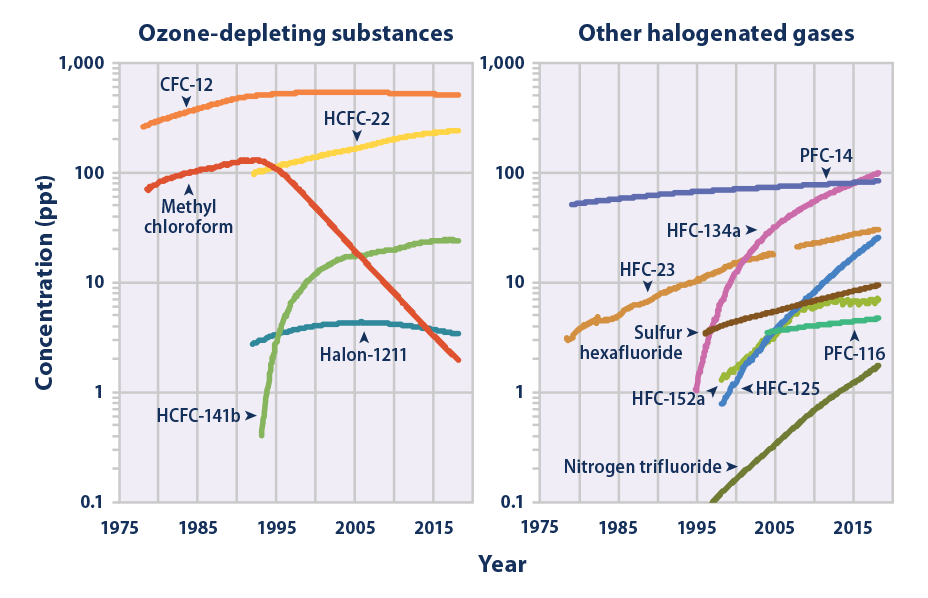



Youxclg0bikhtm
This graph shows the increase in greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations in the atmosphere over the last 2,000 years Increases in concentrations of these gases since 1750 are due to human activities in the industrial eraA greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that takes in (absorbs) and gives off (emits) radiation in the heat (infrared) wavelength range Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth Source National Climatic Data CenterNOAA Paleoclimatology The greenhouse effect occurs as solar No, the coronavirus lockdown did not solve climate change Not even a little bit In fact, the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere surged to




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Annual Ghg Index Aggi
Levels of the two most important anthropogenic greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide and methane, continued their unrelenting rise in despite the economic slowdown caused by the coronavirus pandemic response, NOAA announced today The global surface average for carbon dioxide (CO2), calculated from measurements collected at NOAA's remote samplingMain Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedData Trends in CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O, SF 6 Obs ervation Pack age Marine Boundary Layer Reference Data Archive Products CarbonTracker CO 2 CarbonTracker CH 4 CarbonTracker Lagrange Power of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Index Information Figures Education How CO 2 is Measured Isotope Measurements WMO Standard Gas Comparisons
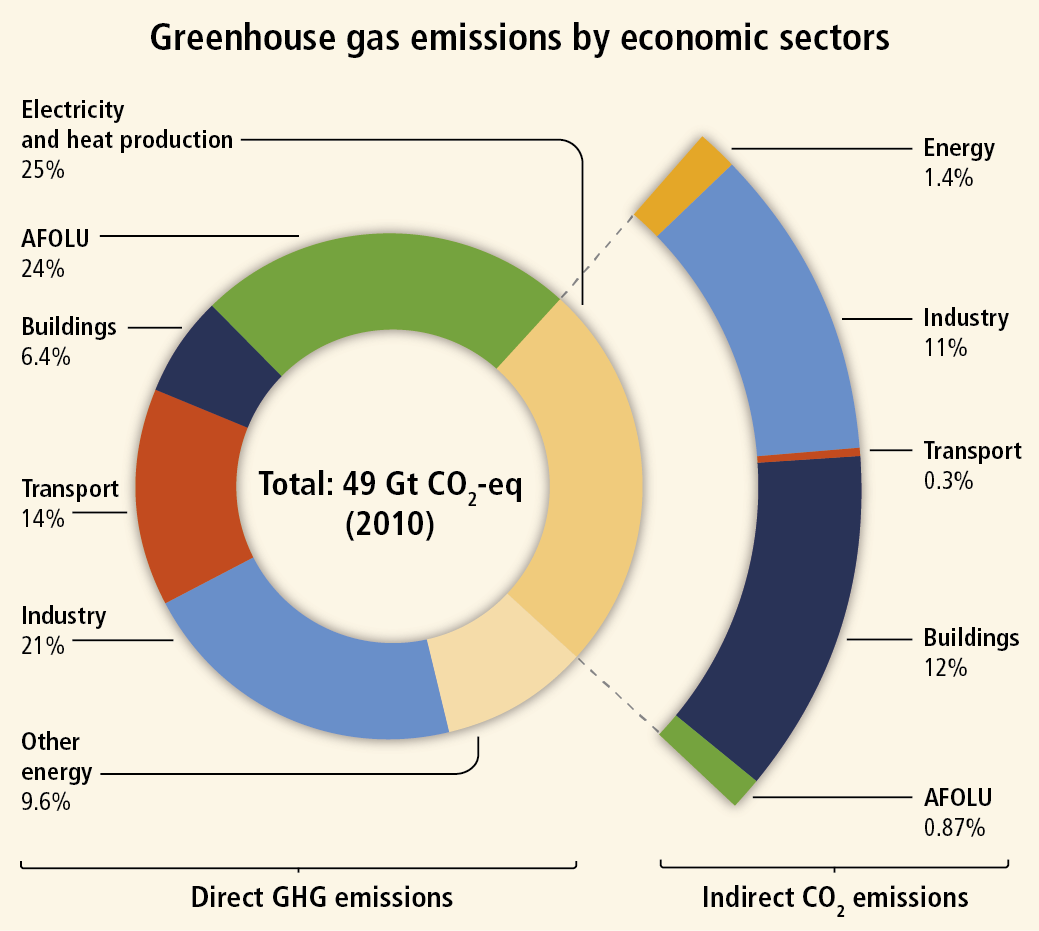



Impact Of Agriculture On Climate Change



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
Human activities produce large amounts of greenhouse gases (GHGs), primarily carbon dioxide (CO 2), and thus contribute to global warmingThe use of fossil fuels is the primary source of CO 2 emissions, but the removal of trees from forested land has also contributed Mature forests, having absorbed CO 2 from the atmosphere while growing, store carbon in wood, These graphs depict the global average abundances of the major, wellmixed, longlived greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, CFC12 and CFC11 from the NOAA global air sampling network plotted since the beginning of 1979Nitrous oxide is a powerful greenhouse gas that lasts for over 100 years in the atmosphere It is best known as laughing gas, but that kind of commercial use makes up only a tiny part of our emissions By far the biggest way we add nitrous oxide to the atmosphere is by growing crops with nitrogenbased fertilizers CFCs Up to 12,690



Greenhouse Gases



The Greenhouse Effect
There are many who think the greenhouse gas content of the atmosphere has increased enormously since the Industrial Revolution The water content of the atmosphere has remained roughly constant The graph below gives the times series for the greenhouse content of the Earth's atmosphere from the first measurements of the CO 2 content (To be continued)Many greenhouse gases occur naturally Carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and nitrous oxide are naturally present in Earth's atmosphere Others, such as chorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), are human made Because of the Industrial Revolution atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations have This imbalance between greenhouse gas emissions and the ability for natural processes to absorb those emissions has resulted in a continued increase in atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases Concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere have increased by about 40% since the mid1800s




Carbon Dioxide Exercise
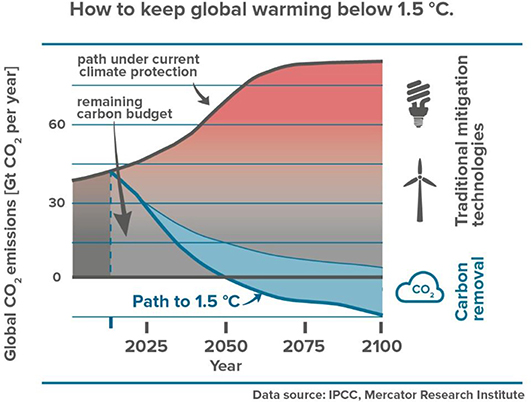



Frontiers The Role Of Direct Air Capture In Mitigation Of Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate
The graph you show is not "The resultant change in outgoing radiation was as follows" as you state What it is the data that has been manipulated to highlight the drops in radiance in the regions of the spectra that are absorbed by CO2 and CH4 (and other trace gases) Adding more greenhouse gas to the atmosphere makes higher, more tenuous The first graph shows monthly means for the last four years plus the current year, and the second graph shows the NOAA timeseries starting in 01, when we have confidence in the data Values for the last year are preliminary pending recalibrations of standard gases and other quality control stepsCombined these three gases comprise more than 995% of all the gas molecules in the atmosphere These gases which are most abundant within the atmosphere exhibit almost no effect on warming the earth and its atmosphere since they do not absorb visible or infrared radiation However, there are minor gases which comprise only a small portion of the atmosphere




Carbon Dioxide Levels Continue At Record Levels Despite Covid 19 Lockdown World Meteorological Organization



Graph Of The Day Antropocene Atmospheric Experiment Ghg Climate Forcing Increased 29 Over Years Bits Of Science
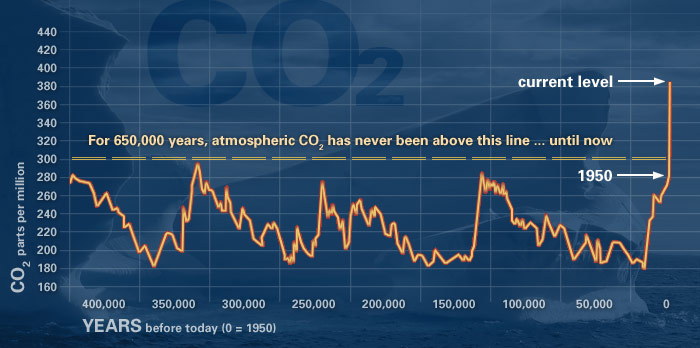
Graphic The relentless rise of carbon dioxide Ancient air bubbles trapped in ice enable us to step back in time and see what Earth's atmosphere, and climate, were like in the distant past They tell us that levels of carbon dioxide (CO 2) in the atmosphere are higher than they have been at any time in the past 400,000 yearsGreenhouse gases due to their very high global warming potentials and long atmospheric lifetimes even if they only exist at a few ppt (see table) Ozone is also a greenhouse gas, but it differs from other greenhouse gases in several ways The effects of ozone depend on its altitude, or where the gas is located vertically in the atmosphere The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,




Global Atmospheric Co2 Greenhouse Gases Graphing Global



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
This graph ( source data) shows differences from the longterm average global ocean heat content () in the top 700 meters of the ocean Averaged over Earth's surface, the 1993–19 heatgain rates were 036 (±006) to 041 (±004) watts per square meter for depths from 0–700 meters, and 014 (±004) to 032 (±003) for depthsThe graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around the world, greenhouse gases become globally mixed, which means the concentration of a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide is roughly the same no matter where you Carbon dioxide Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth




This Graph Shows The Increasing Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases In Download Scientific Diagram
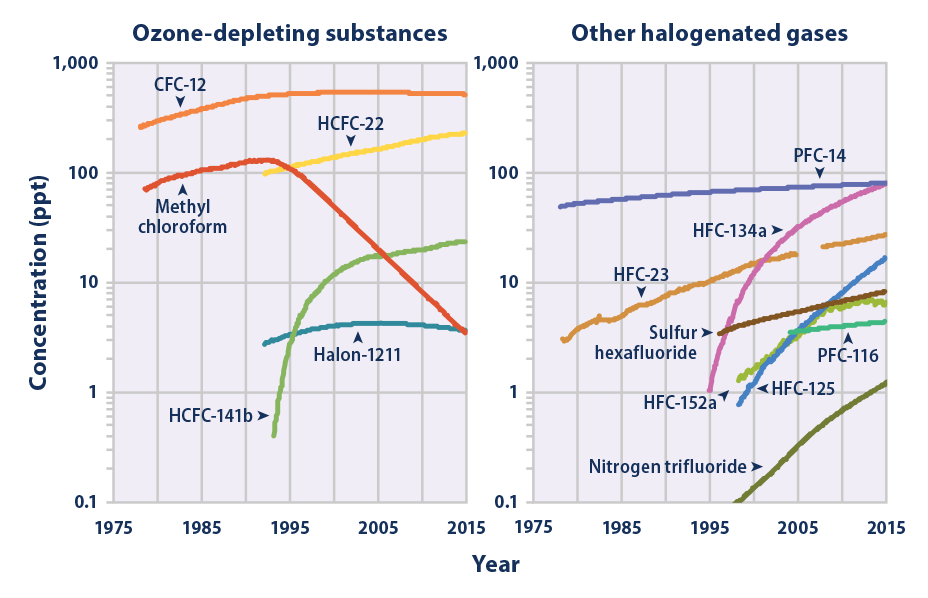



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
Water vapor is also the most important greenhouse gas in the atmosphere Heat radiated from Earth's surface is absorbed by water vapor molecules in the lower atmosphere The water vapor molecules, in turn, radiate heat in all directions Some of the heat returns to the Earth's surface Thus, water vapor is a second source of warmth (in additionTo slow down – with the eventual aim of halting – rising global temperatures, we need to stabilize concentrations of CO 2 and other greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere 9 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth's history 10 It's important to note that there is 'lag' between atmospheric The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight At night, Earth's surface cools, releasing heat back into the air But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere




Projected Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Source Graph Download Scientific Diagram



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
This graph shows the heating imbalance in watts per square meter relative to the year 1750 caused by all major humanproduced greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12, and a group of 15 other minor contributors
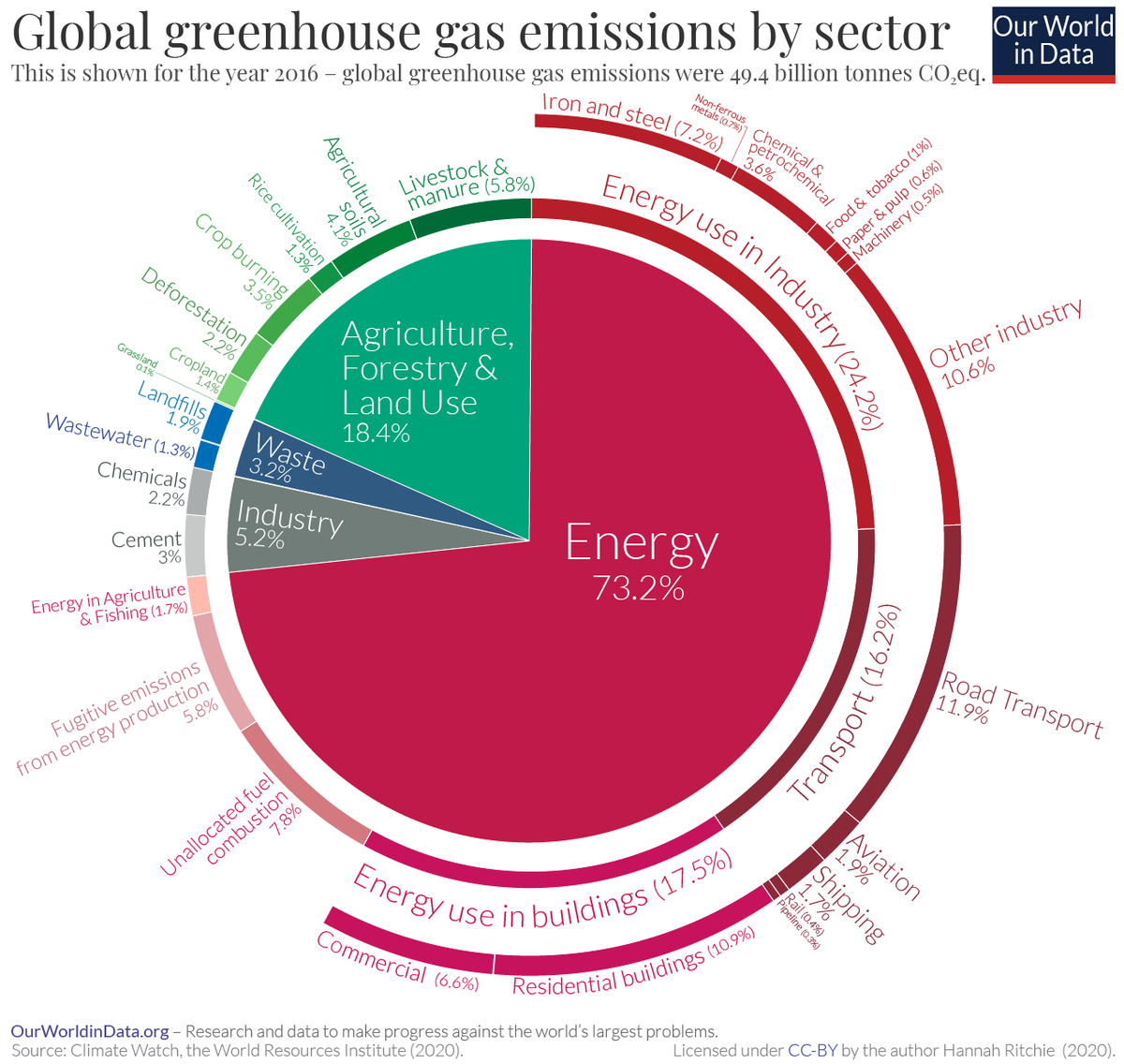



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector



Q Tbn And9gcqx8qqb7vyjubela12bb Jefr3jui9po9norhhsaq Qhlnrfuaa Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central



Climate Related Charts And Graphs



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



1




Predictions Of Future Global Climate Ucar Center For Science Education




Climate Literacy Quiz




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja




How The World Passed A Carbon Threshold And Why It Matters Yale 60




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16185122/gw_graphic_pie_chart_co2_emissions_by_country_2015.png)



Climate Change Animation Shows Us Leading The World In Carbon Emissions Vox
.png)



Fact Sheet The Growth In Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Commercial Aviation White Papers Eesi



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Global Climate Change Explorer Atmosphere Exploratorium



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Q Tbn And9gcsud8qrpbvfrrwlzfbkcia7ejm3in8xid1hdwmfio Rdlvyoqxe Usqp Cau



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



Ghgs Descriptions Sources In California California Air Resources Board



Kenl Qwhyysavm



Tracking Progress American University Washington Dc
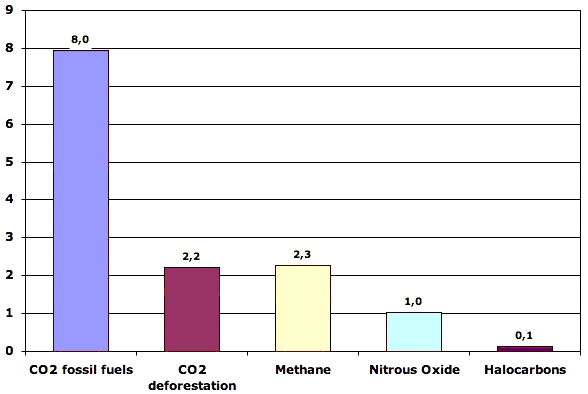



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
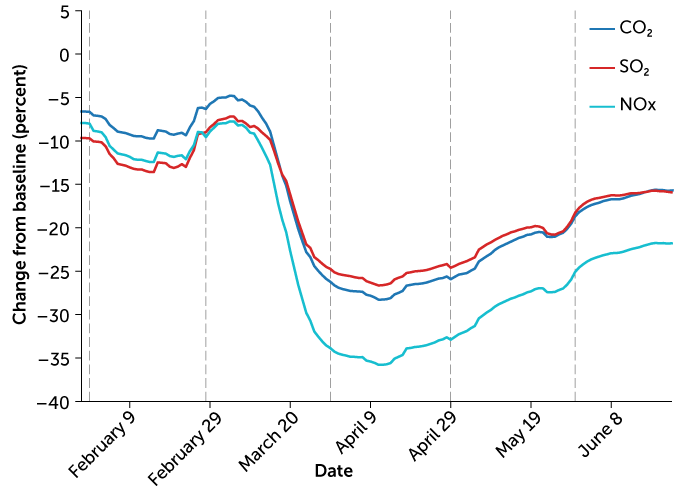



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus




Climate Change And Agriculture Niwa




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming
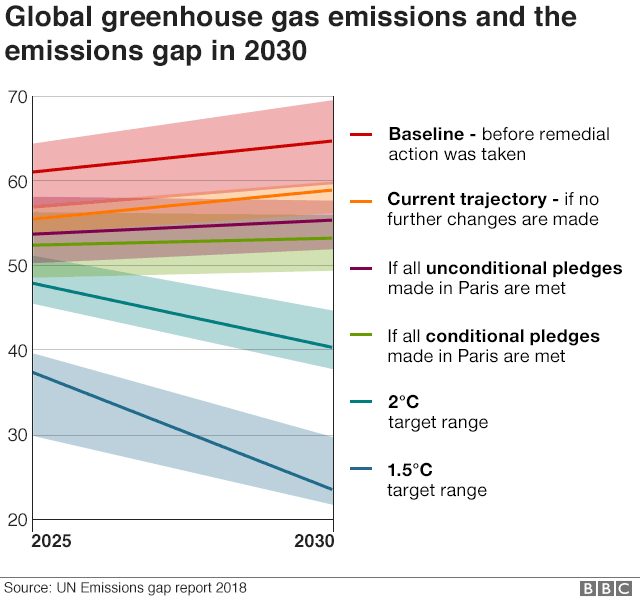



Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau
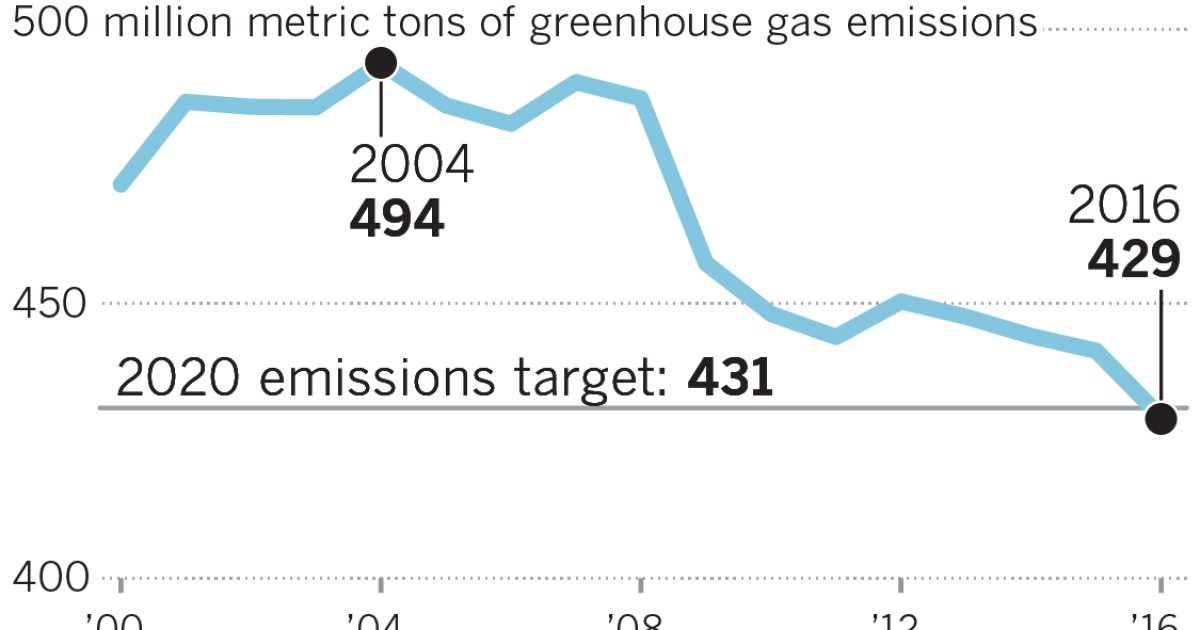



California Hit Its Climate Goal Early But Its Biggest Source Of Pollution Keeps Rising Los Angeles Times
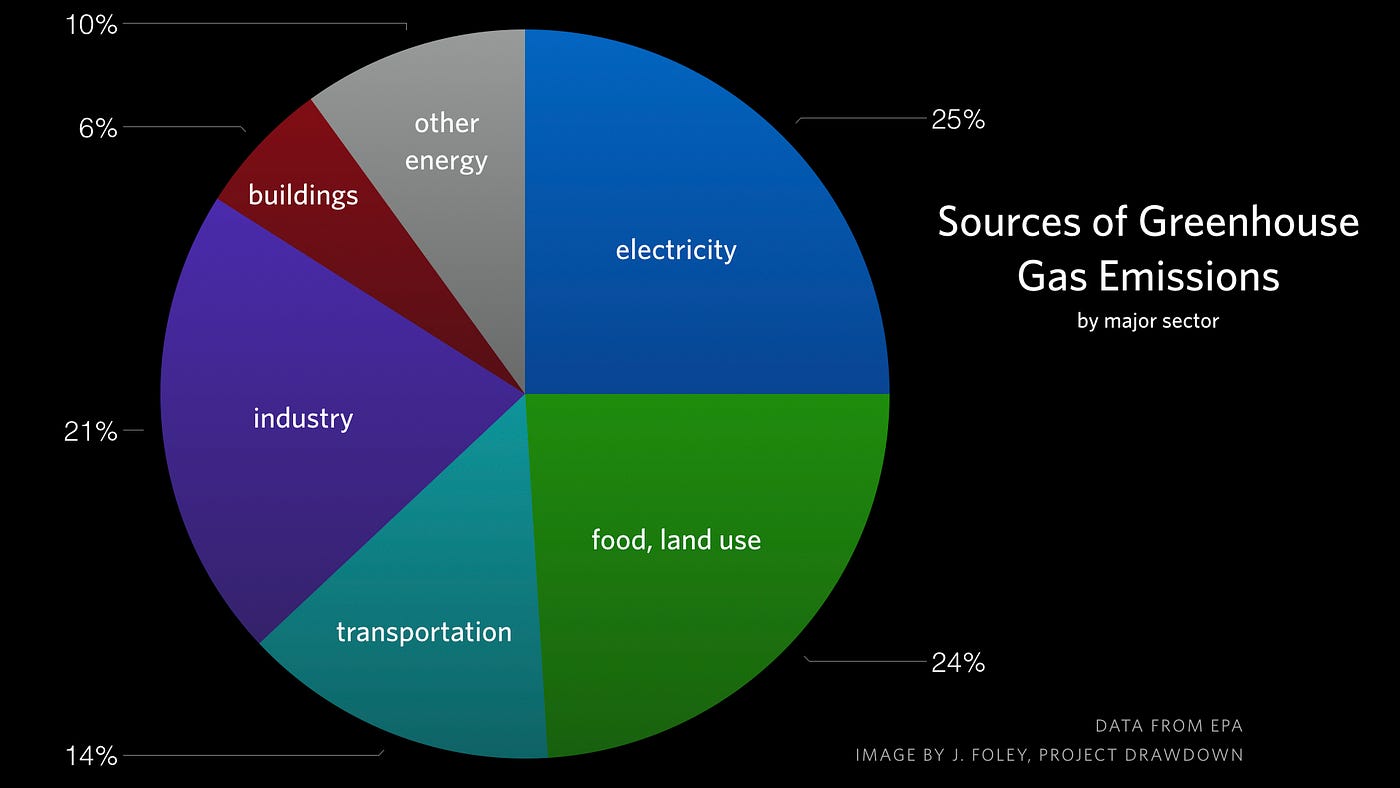



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Air Composition Of Earths Atmosphere By Volume Bar Graph Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock




Changes Since The Industrial Revolution American Chemical Society
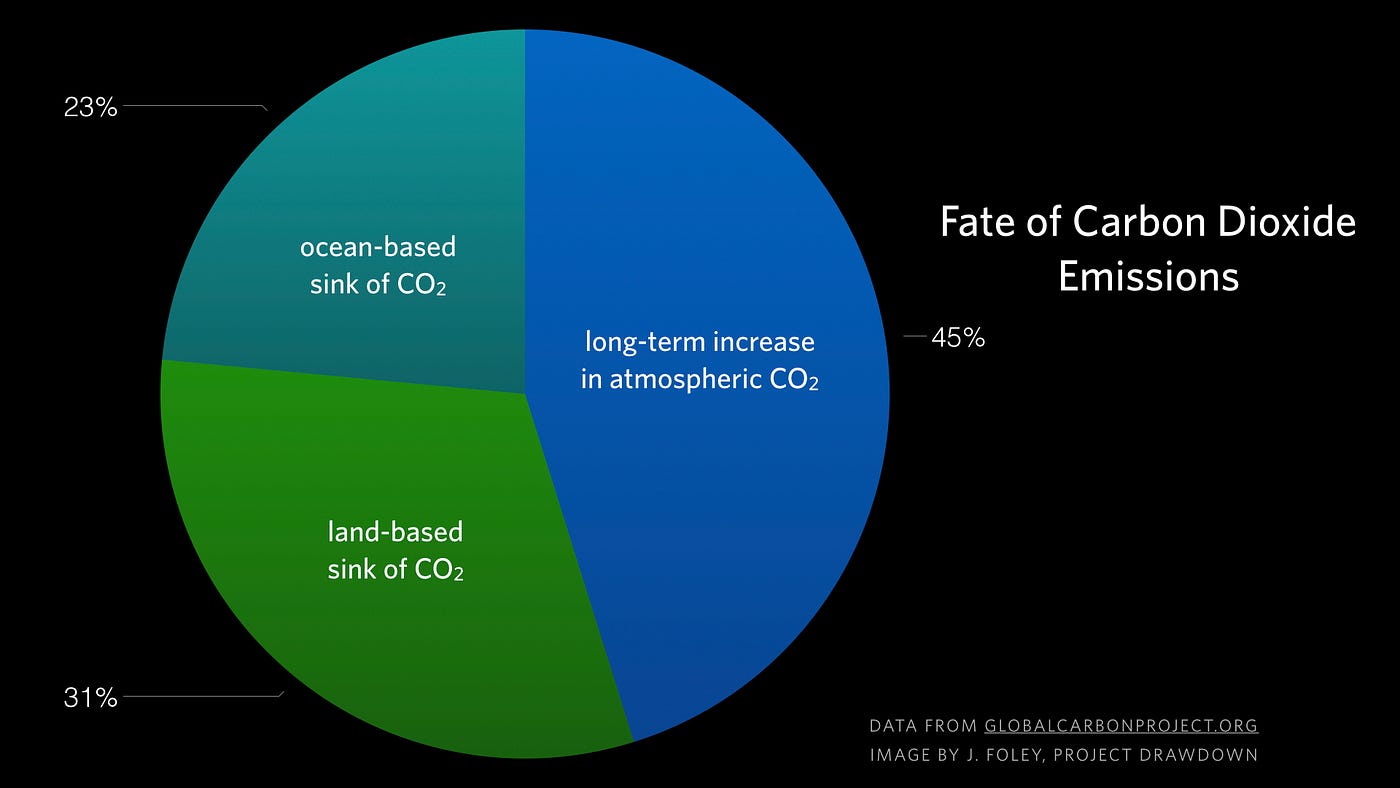



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Despite Pandemic Shutdowns Carbon Dioxide And Methane Surged In Welcome To Noaa Research



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature



Down To Earth Climate Change Resources




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization




Methane And Climate 10 Things You Should Know Darrin Qualman
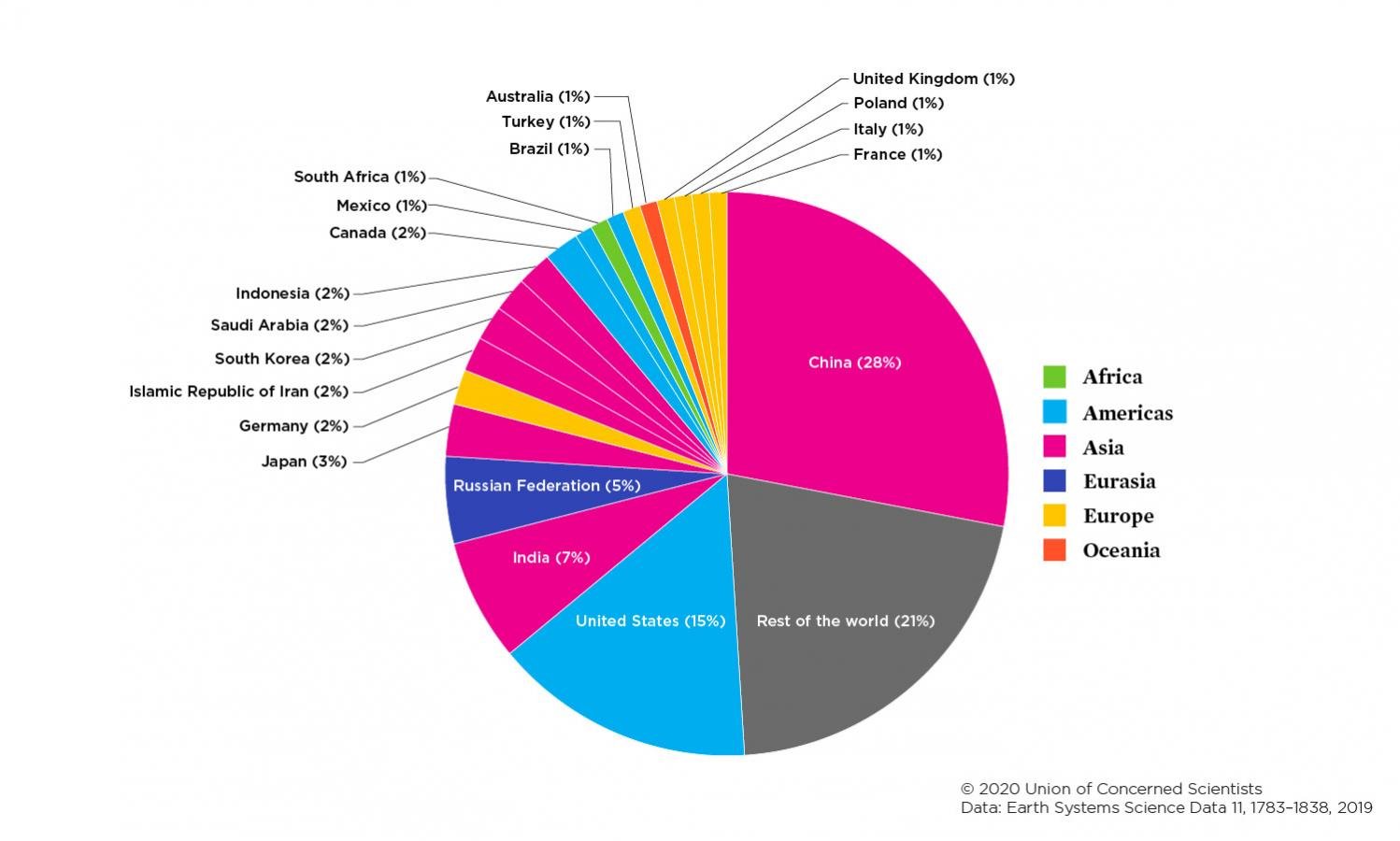



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists




Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From



Carbon Dioxide Vital Signs Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Keeling Curve History Importance Facts Britannica
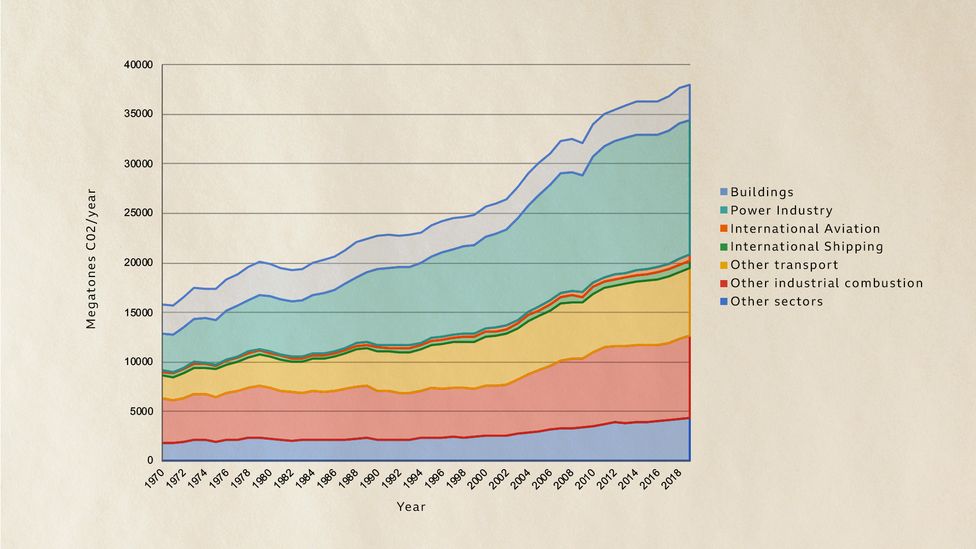



The State Of The Climate In 21 c Future
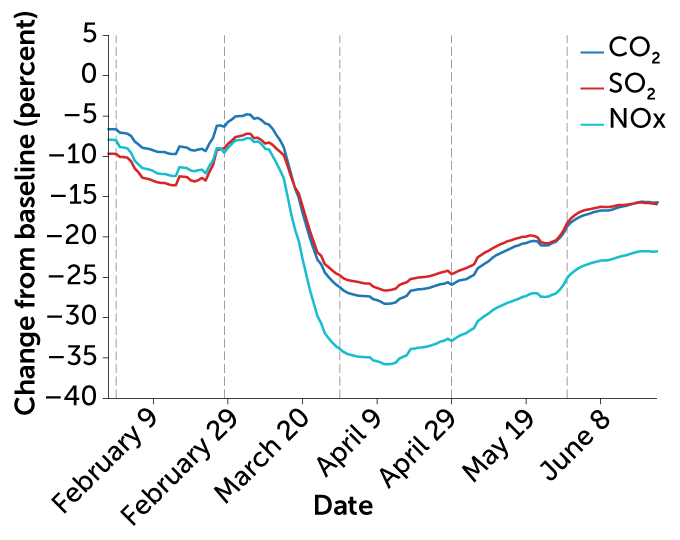



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News
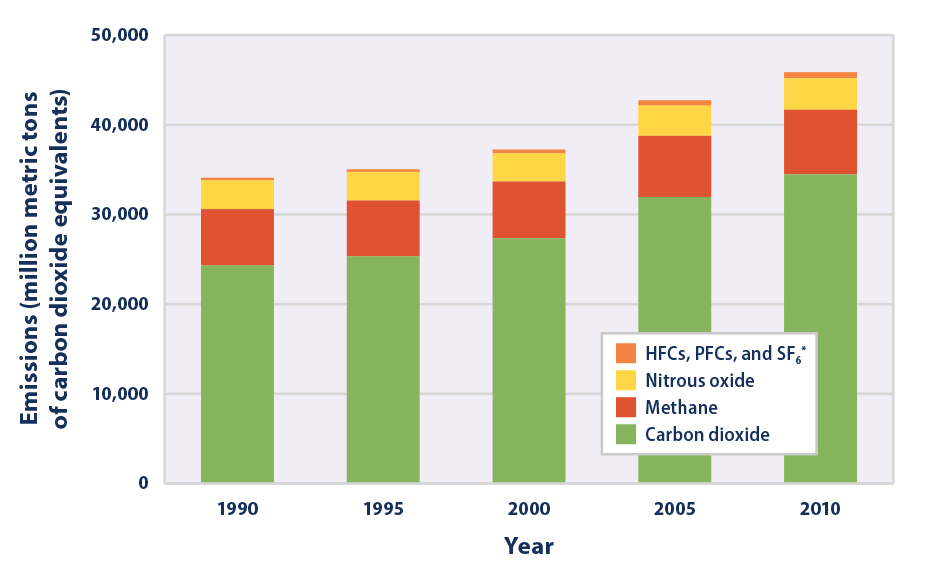



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
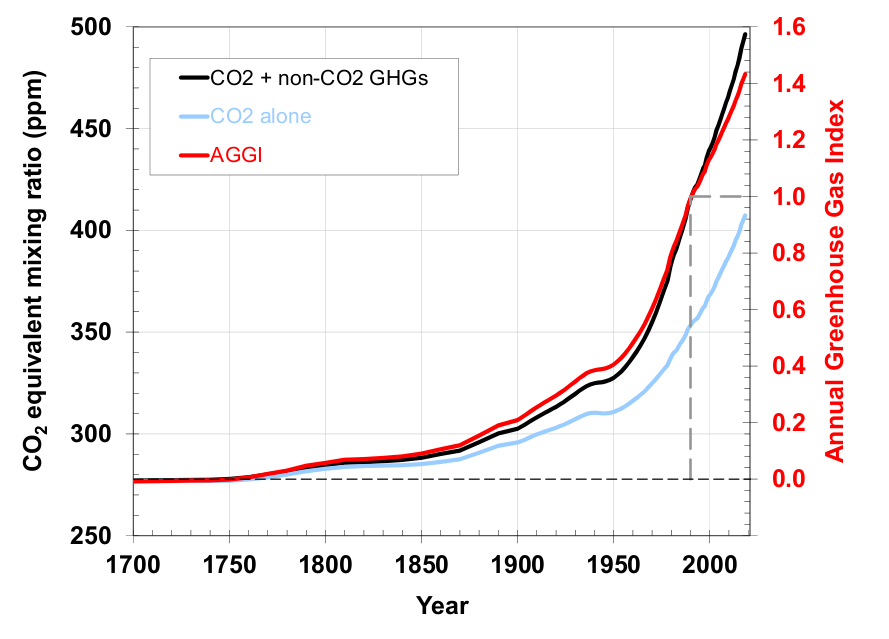



Graph Of The Day Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index 1700 18 Desdemona Despair
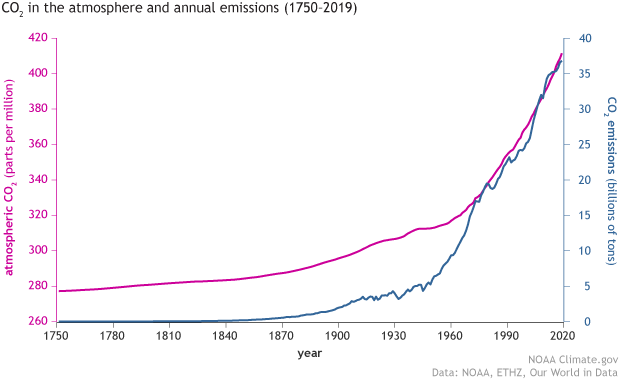



Climate Change Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Noaa Climate Gov




The Very Simple Climate Model Activity Print Activity Ucar Center For Science Education




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
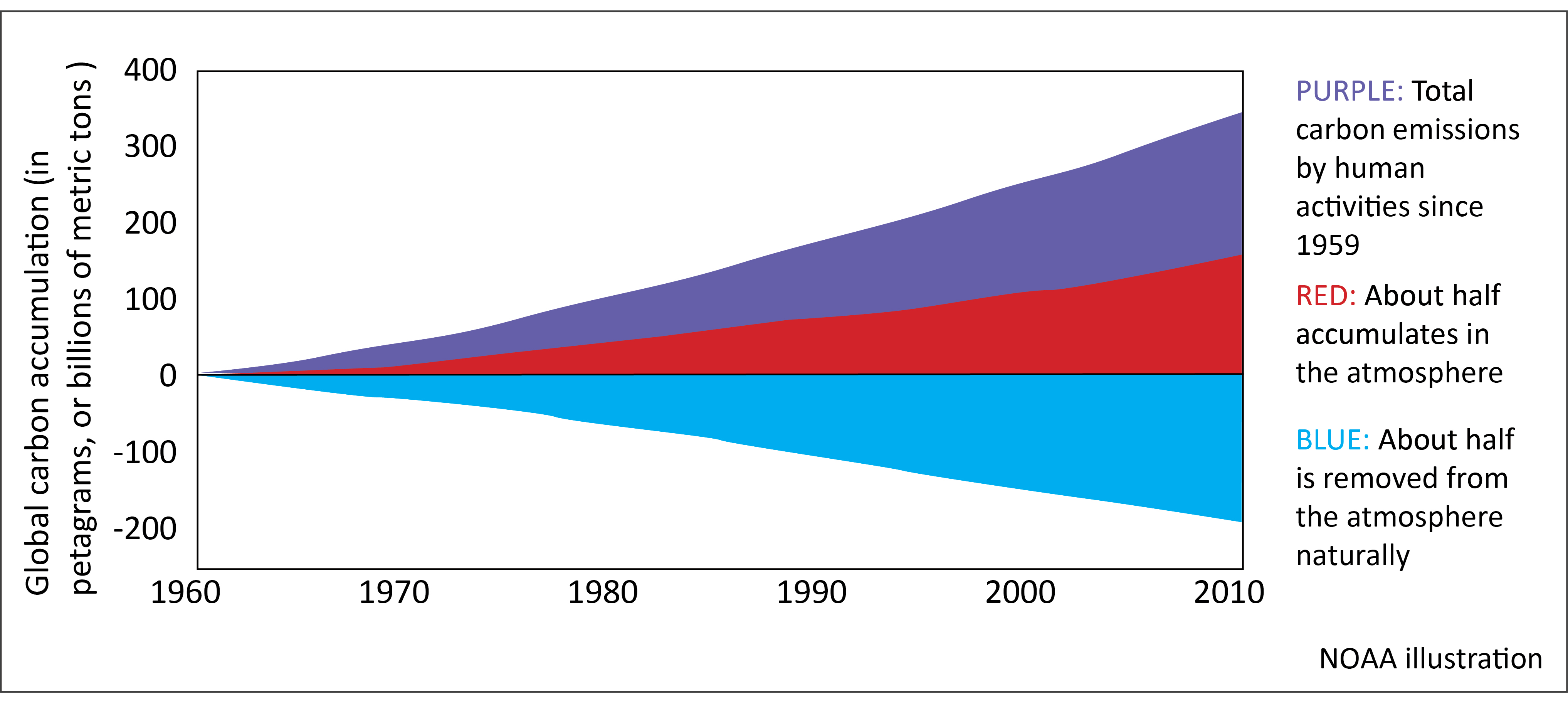



Carbon Uptake Has Doubled Over Last 50 Years But Where Is It Going Carbon Brief




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate



Temperatures Climate Action Tracker



Attribution Of Recent Climate Change Wikipedia
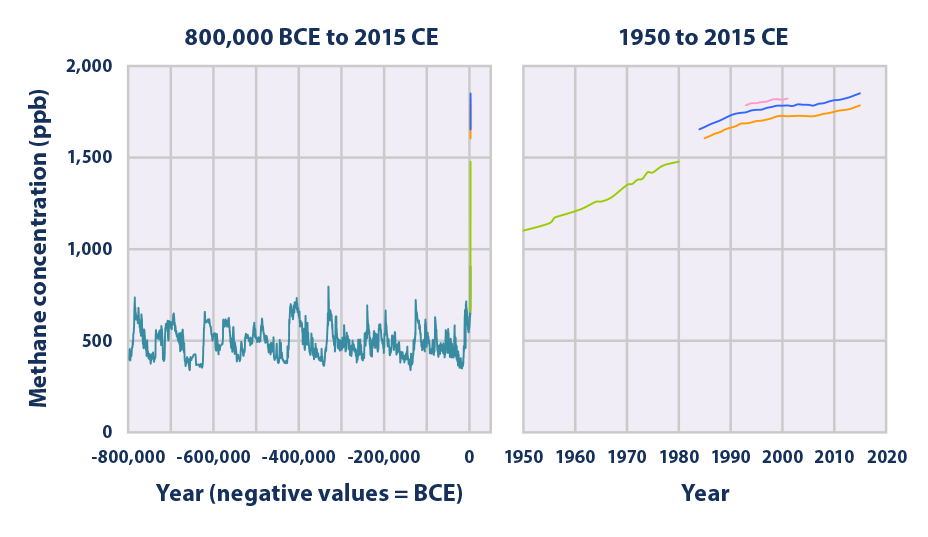



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa




What Are The Greenhouse Gas Emissions Of A Mini Grid Project And How Are They Calculated Mini Grids Support Toolkit Energy U S Agency For International Development
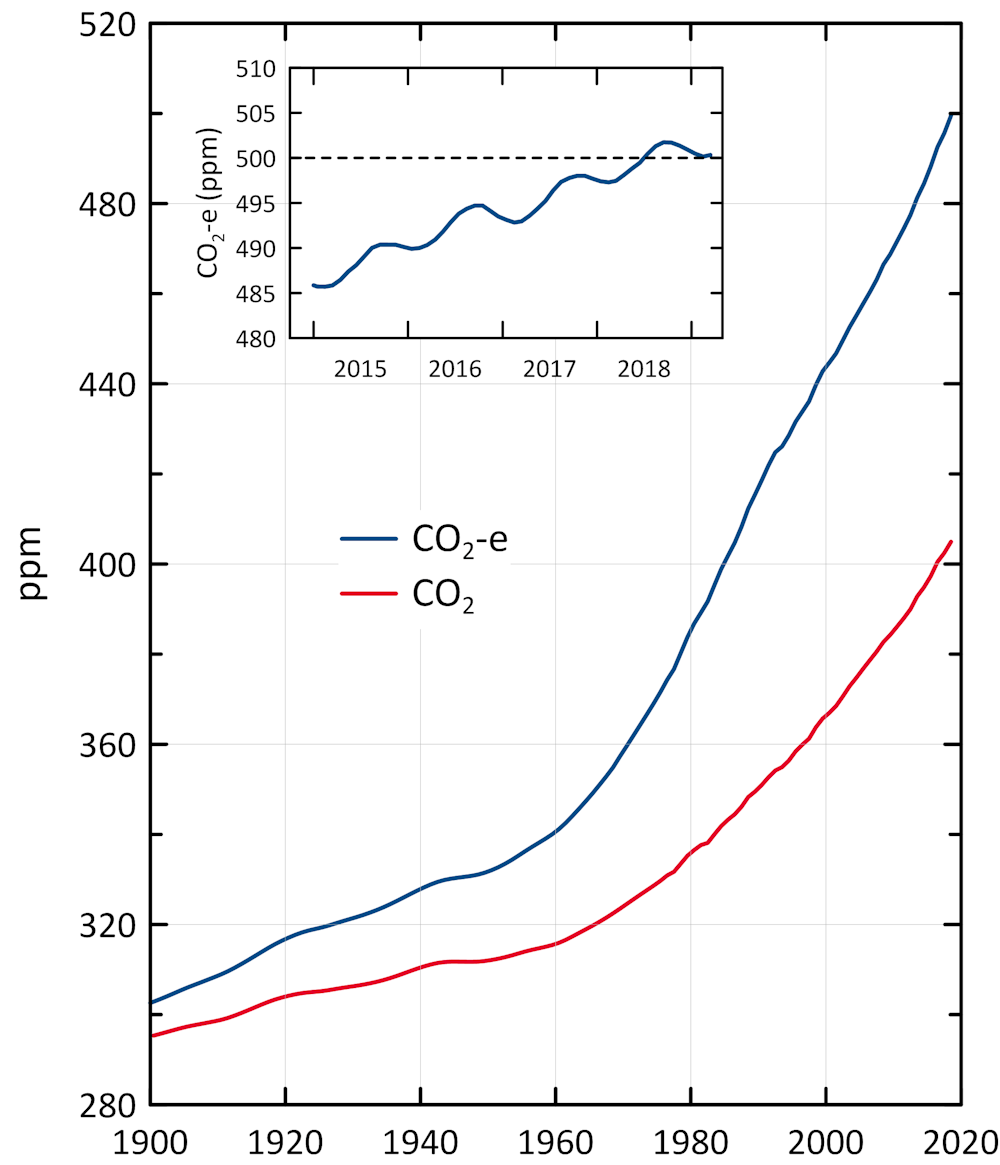



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised
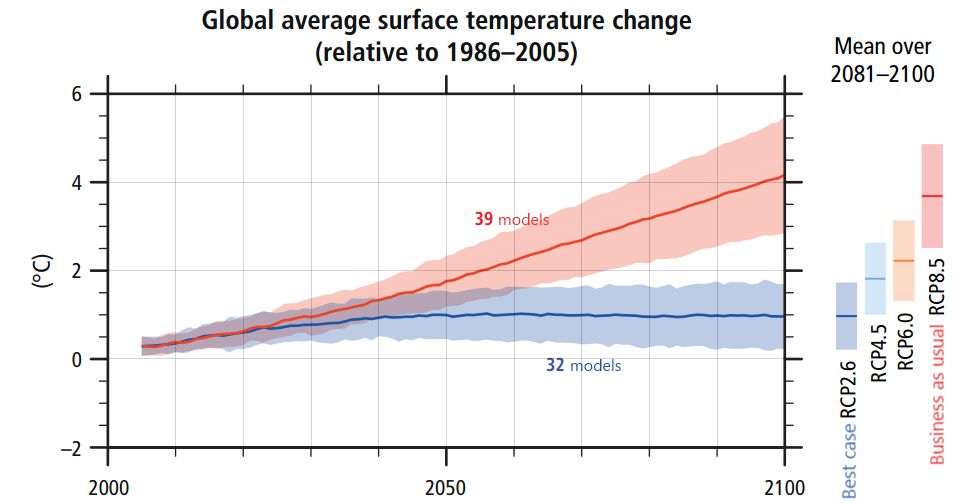



How Could Global Warming Accelerate If Co2 Is Logarithmic




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
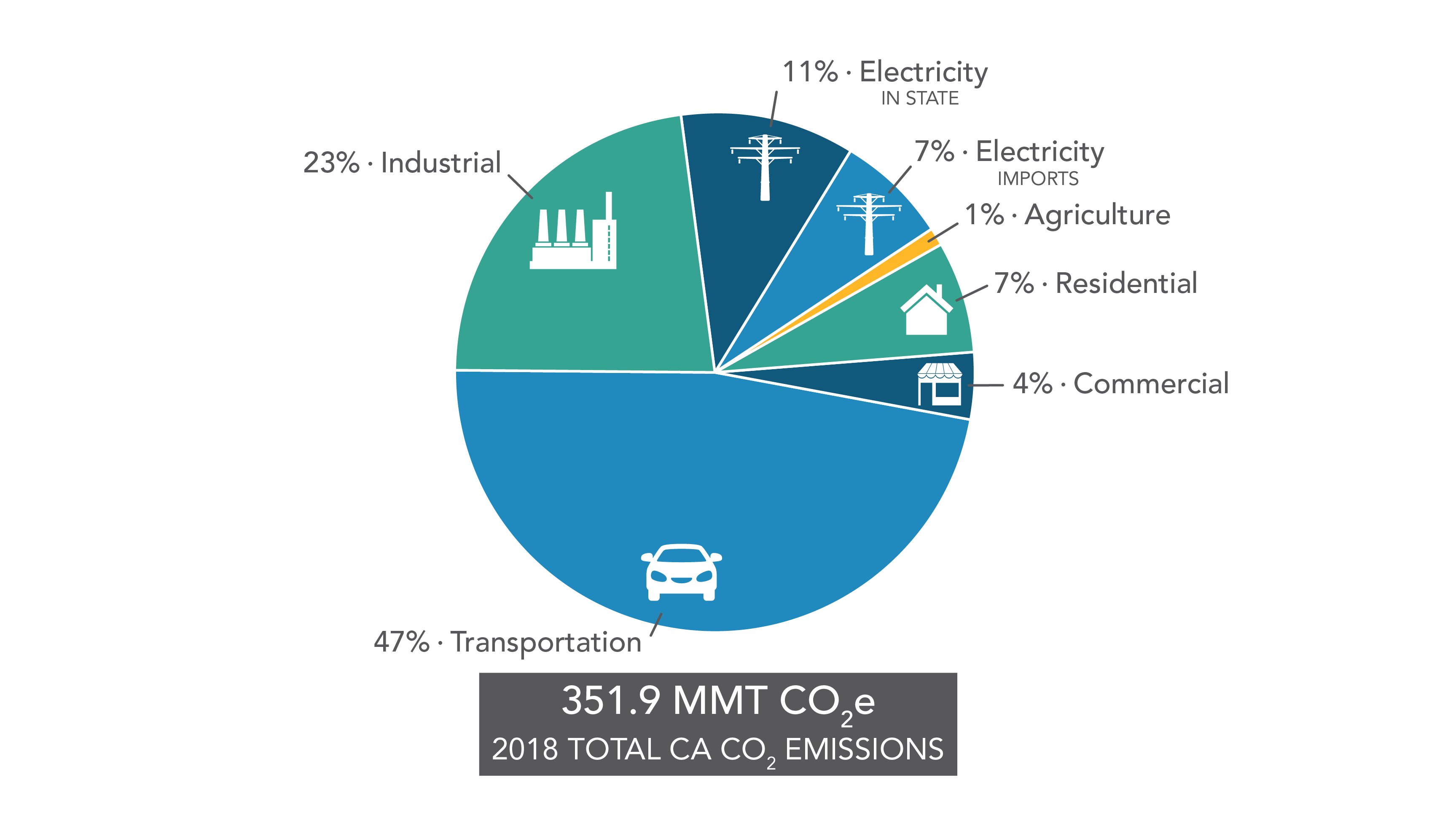



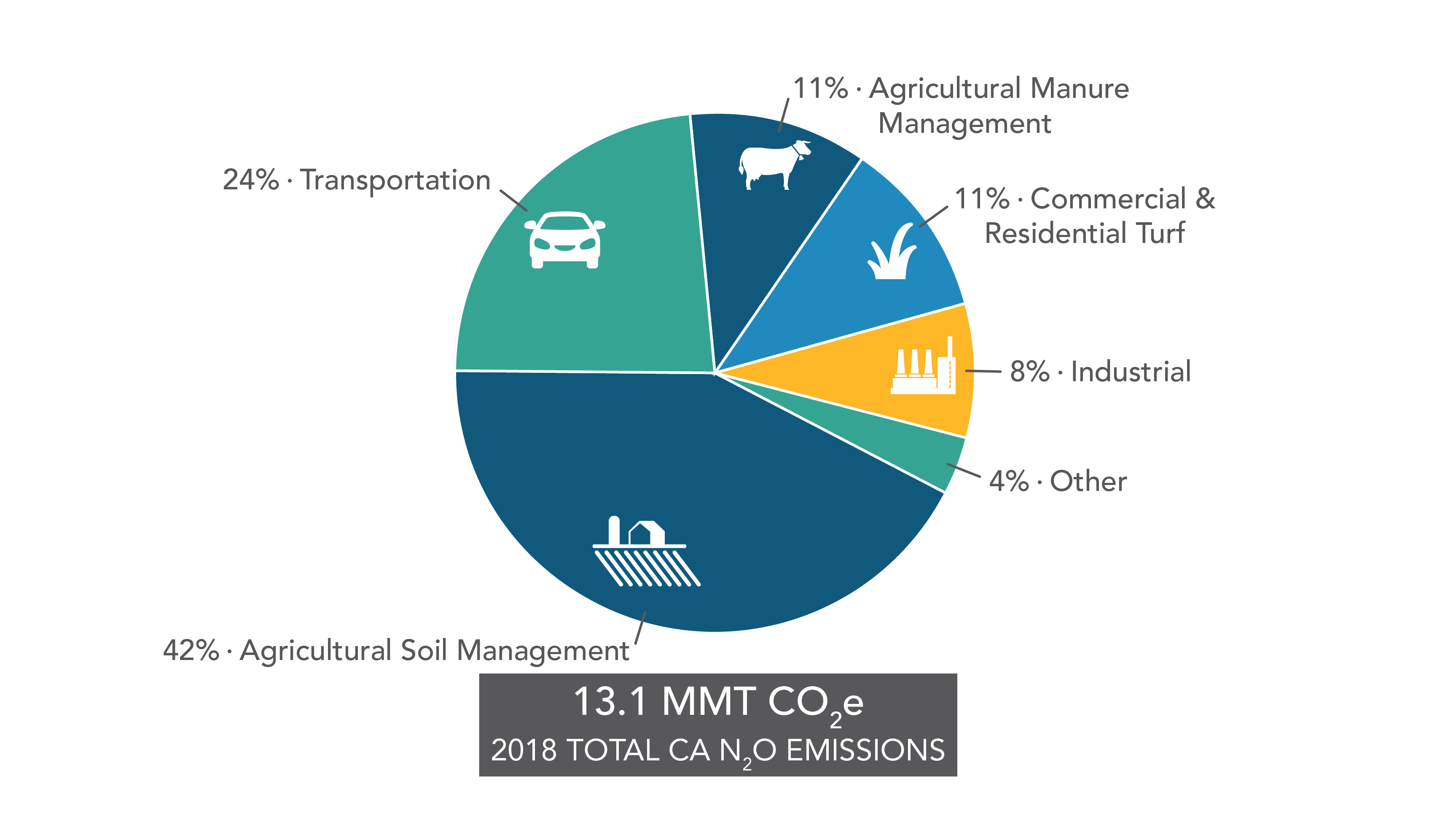
Ghgs Descriptions Sources In California California Air Resources Board
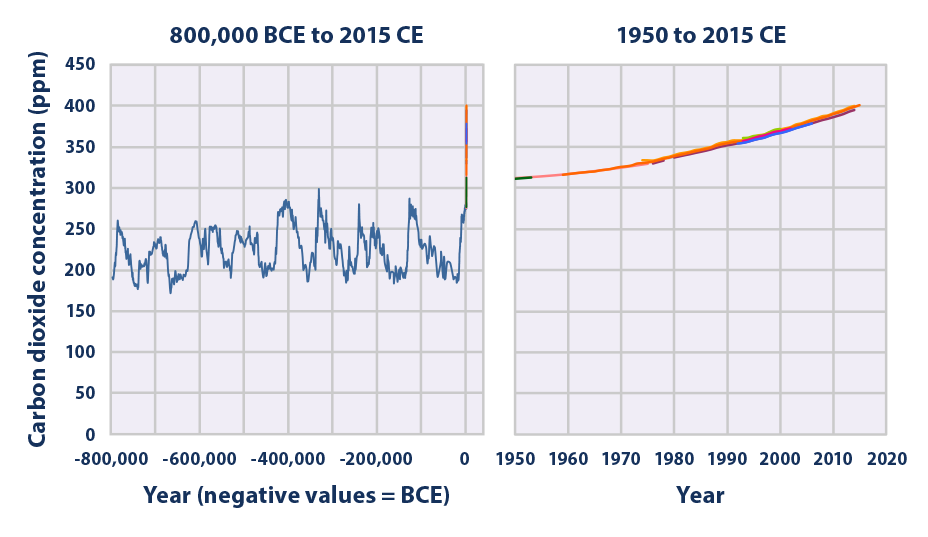



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
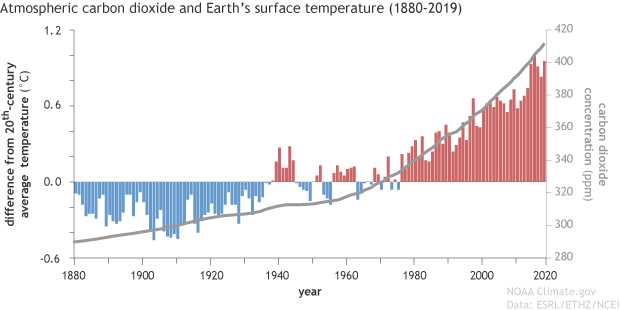



If Carbon Dioxide Hits A New High Every Year Why Isn T Every Year Hotter Than The Last Noaa Climate Gov



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Graph Of The Day Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Aggi 1700 15 Desdemona Despair




The Role Of Animal Agriculture On Greenhouse Gas Emissions




The Keeling Curve National Geographic Society




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society



Atmo336 Fall




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Population Growth Vs Emissions Growth Serendipity




This Graph Shows The Increase In Greenhouse Gas Ghg Concentrations In Download Scientific Diagram




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change



Greenhouse Gases



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿